REGISTRO DOI: 10.69849/revistaft/ch10201910180808
Glayston André Melo da Silva
Abstract
The advent of digital platforms has revolutionized how individuals interact with audiovisual content and music, leading to significant changes in consumption patterns, user behavior, and industry dynamics. Streaming services like Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and Spotify have democratized access to a vast array of content, offering personalized experiences that cater to individual preferences. This shift has not only redefined media consumption practices but also influenced daily routines and habits, with phenomena like binge-watching becoming increasingly common. The entertainment industry, which once viewed consumers as passive recipients, now faces a paradigm shift where users actively participate in shaping their media experiences. The widespread use of internet tools and the digitization of audiovisual signals have facilitated the free exchange of content, leading to an exponential increase in available titles and altering the traditional relationship between audiences and media. In the music industry, the rise of streaming services has sparked debates over their impact on recorded music revenue. Studies reveal that while streaming may displace traditional sales, it can still increase overall revenue and reduce piracy. Furthermore, the adoption of platforms like Spotify has led to an increase in music consumption, variety, and discovery, although it has also influenced the repetition of new music discoveries. Valiati’s (2020) research on Netflix users highlights the formation of interconnected consumption flows, where continuous content availability and routinized access shape user engagement. This transformation underscores the evolving nature of digital consumption, with significant implications for platforms, content creators, and consumers alike.
Keywords: Digital Platforms; Streaming Services; Audiovisual Consumption; Binge-Watching; Music Industry Revenue.
Audiovisual consumption on digital platforms has significantly reshaped how individuals engage with content and entertainment. The advent of streaming platforms like Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and Disney+ has democratized access to a vast array of audiovisual options, enabling users to choose what to watch, when, and where they want. This shift has not only altered media consumption practices but also redefined the daily routines and patterns of users.
Streaming platforms offer a personalized experience, tailoring content recommendations based on individual preferences and viewing history. This model, driven by subscriptions or pay-per-view, provides users with extensive catalogs of movies, series, and TV shows that can be accessed on a variety of devices, from smartphones to smart TVs. The flexibility and convenience offered by these platforms have been key factors in their rapid growth.
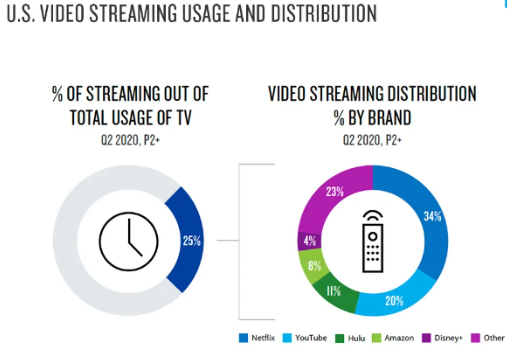
Figure 1: U.S. vídeo streaming usage and distribution.
Source: Nielsen Streaming Meter (2020).
One of the hallmark features of streaming consumption is the personalization of viewing practices. Algorithms that recommend content, the ability to create custom playlists, and functions that track viewing progress are all examples of how these platforms shape and influence user choices. These tools make it easier to navigate the vast amount of content available, encouraging deeper engagement as users discover new favorites and immerse themselves in series and films that align with their tastes.
A distinctive aspect of this new consumption model is the phenomenon of “binge-watching,” where users watch multiple episodes or even entire seasons of a series in one sitting. This practice has fundamentally altered traditional media consumption rhythms, creating new dynamics of engagement and deeper involvement with content. However, the vast array of choices can also lead to “choice overload,” where the abundance of options becomes overwhelming, making it difficult for users to decide what to watch. Moreover, the continuous availability of content can lead to excessive consumption, potentially impacting mental health and well-being.
The entertainment industry, which traditionally viewed viewers as passive recipients, has had to adapt to a new paradigm where consumers are active participants. The digitization of audiovisual signals, along with the widespread use of Internet tools such as P2P networks and streaming services, has facilitated the free exchange of audiovisual products, often bypassing traditional commercial restrictions. This shift has led to an exponential increase in the availability of titles for immediate, low-cost consumption, particularly in television series.
This change in consumption patterns, particularly the rise of binge-watching, has also affected users’ daily habits, influencing everything from sleep schedules to general well-being. Research by Pérez and Díaz (2017) delves into this new model of audiovisual consumption, focusing on how binge-watching impacts young students’ daily routines, academic performance, and overall well-being. Their study highlights the active role viewers now play in shaping their media experiences, with significant implications for both individual and societal behaviors.
In the music industry, similar shifts are occurring. Aguiar and Waldfogel’s (2017) study examines the impact of music streaming services on recorded music revenue, a topic that has sparked both optimism and concern. Their research reveals that while streaming may displace traditional music sales, it can still increase total industry revenue if the payments per stream are high enough to offset the decline in sales. Additionally, the study shows that streaming reduces music piracy, with the gains in streaming revenue roughly balancing out the losses from decreased sales.
Similarly, the study by Datta, Knox, and Bronnenberg explores the effects of adopting streaming services like Spotify on individual music consumption behavior. Their research, which utilizes a unique dataset tracking consumer listening habits, finds that streaming leads to increased music consumption in terms of both quantity and variety, as well as greater discovery of new music. However, it also notes a decrease in the repetition of new discoveries, a finding consistent with the free marginal variety offered by platforms like Spotify.
Valiati’s (2020) research on audiovisual consumption further explores these evolving practices, focusing specifically on Netflix users. Her study reveals the formation of interconnected consumption flows, where users and platforms are in a recursive relationship: continuous content availability on the platform is met with routinized and fragmented access by users. This dynamic supports the maintenance and growth of the platform’s established structure, illustrating how digital consumption practices are reshaping the entertainment landscape on multiple levels.
The study by Wlömert and Papies (2016) delves into how digital platforms have revolutionized audiovisual and music consumption, highlighting a significant departure from traditional passive media consumption models. Their research underscores how streaming services, such as Netflix and Spotify, have empowered users with unprecedented control over their content choices, facilitating a more active and personalized engagement. This transformation is evidenced by the shift towards binge-watching and the vast array of content available at users’ fingertips, which has fundamentally changed media consumption practices. The study further explores how these platforms have redefined industry dynamics, presenting both opportunities and challenges for traditional revenue models and consumer behavior.
The findings of Wlömert and Papies (2016) also emphasize the ongoing evolution of digital platforms and their growing influence on user habits and industry structures. As these platforms continue to adapt and innovate, they will likely further reshape how content is accessed and valued. The interplay between user autonomy, content availability, and platform strategies will be crucial in determining future trends in media consumption. Their research suggests that understanding these dynamics is essential for anticipating the future landscape of digital media and its implications for both consumers and industry stakeholders.
The transformation of audiovisual and music consumption through digital platforms marks a profound shift in how content is accessed, experienced, and valued. This evolution highlights the active role of users in shaping their media interactions, a stark contrast to the passive consumption models of the past. Streaming services have not only democratized access to a vast array of content but also redefined industry dynamics, challenging traditional revenue models and influencing consumer behavior in unprecedented ways. The rise of personalized content delivery and phenomena like binge-watching illustrate the deep integration of these platforms into daily life, while the music industry’s adaptation to streaming underscores the complex balance between traditional sales and new revenue streams.
As digital platforms continue to evolve, their impact on user practices, industry structures, and cultural consumption patterns will likely deepen, prompting further exploration into the implications of this ongoing paradigm shift. The interplay between content availability, user autonomy, and platform strategies will remain central to understanding the future of media consumption in a digitally-driven world.
References
Aguiar, L., & Waldfogel, J. (2017). As streaming reaches flood stage, does it stimulate or depress music sales?. International Journal of Industrial Organization, 57, 278-307. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJINDORG.2017.06.004.
Datta, H., Knox, G., & Bronnenberg, B. (2017). Changing Their Tune: How Consumers’ Adoption of Online Streaming Affects Music Consumption and Discovery. Behavioral Marketing eJournal. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2782911.
Pérez, J., & Díaz, M. (2017). Nuevos modelos de consumo audiovisual: los efectos del binge-watching sobre los jóvenes universitarios. adComunica. Revista Científica de Estrategias, Tendencias e innovación en Comunicación, 201-221. https://doi.org/10.6035/332.
Valiati, V. (2020). Consumo audiovisual em plataformas digitais: a configuração de práticas e fluxos na rotina de usuários da Netflix. , 194-206. https://doi.org/10.1590/1982-25532020346644.
Wlömert, N., & Papies, D. (2016). On-demand streaming services and music industry revenues — Insights from Spotify’s market entry. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 33, 314-327. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJRESMAR.2015.11.002.
