REGISTRO DOI: 10.69849/revistaft/dt10202505281222
Lilian Cunha1
Abstract
The automation of accounting processes has become an essential tool for businesses aiming to enhance operational efficiency and reduce human error. n8n, an open-source automation platform, presents an accessible and cost-effective solution for small businesses looking to streamline their accounting workflows. This article explores the possibilities, limitations, and impacts of using n8n for accounting automation in small enterprises. It highlights the flexibility of n8n in automating tasks such as invoicing, data entry, and reconciliation, while also discussing the challenges of integrating third-party systems, ensuring data security, and complying with regulatory requirements. The potential benefits, including cost savings, increased efficiency, and better financial decision-making, are examined, along with the impact on accounting job roles and employee skills. Overall, n8n offers a promising solution for small businesses, provided it is implemented with the necessary technical expertise and security precautions.
Keywords: Accounting automation, n8n, Small businesses, Workflow automation, Financial management.
In recent years, the accounting industry has undergone significant changes driven by the adoption of automation technologies. Among the various automation tools available, n8n, an open-source platform, has gained attention for its ability to automate a wide range of business processes, including accounting tasks. This article examines the possibilities, limitations, and potential impacts of using n8n for accounting automation in small businesses.
A key advantage of using n8n for accounting automation is its flexibility. The platform allows users to create custom workflows through a no-code interface, making it accessible even to small businesses with limited technical resources. This feature enables business owners and accounting teams to automate various tasks such as invoice generation, data entry, and reconciliation. By integrating n8n with popular accounting software such as QuickBooks or Xero, businesses can streamline their financial workflows and reduce the potential for human error (Brynjolfsson & McAfee, 2014). Moreover, n8n’s open-source nature makes it a cost-effective solution, as small businesses can implement automation without incurring significant licensing fees often associated with commercial software (Hahn et al., 2020).
Despite its advantages, there are several limitations to consider when using n8n for accounting automation. One notable challenge is the need for integrations with third-party services. Although n8n supports a wide range of integrations, not all accounting software or business applications may be compatible, which could limit its effectiveness in certain scenarios. Small businesses may also face challenges in customizing workflows to fit specific accounting practices or industry requirements, potentially requiring additional technical expertise or development of custom nodes (Jain et al., 2019). Without the necessary in-house technical skills, businesses may struggle to optimize the tool to its fullest potential.
Another limitation of n8n for accounting automation is the importance of ensuring data security and compliance. Automating accounting processes introduces the risk of exposing sensitive financial information if adequate security measures are not implemented. While n8n provides security features such as user authentication and encryption, small businesses must take additional precautions to ensure that their workflows comply with relevant data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union (Schwab et al., 2018). For small businesses without dedicated compliance resources, this can be a significant challenge.
The potential impact of accounting automation on small businesses is profound. Automating routine tasks frees up valuable time, enabling accounting professionals to focus on higher-value activities such as financial analysis, strategic planning, and advising business owners. Moreover, automation provides real-time access to financial data, which can enhance decision-making and improve the accuracy of financial reporting (Chui et al., 2017). For small businesses, this can lead to improved financial management, better cash flow forecasting, and enhanced agility in responding to market changes.
However, the adoption of automation tools like n8n may also have implications for the workforce. As automation takes over repetitive tasks, the role of accountants may shift toward more complex and value-added activities. While this could lead to a reduction in demand for entry-level accounting positions, it could also create opportunities for professionals to specialize in areas such as financial analysis, consulting, and data science (Brynjolfsson & McAfee, 2014). For small businesses, this shift highlights the need for ongoing employee training and development to ensure that the workforce remains adaptable in an increasingly automated environment.
The flowchart illustrates the structured process of implementing accounting automation using n8n in small businesses. It begins with the identification of a need for greater accounting efficiency, leading to the exploration of n8n as a flexible and cost-effective automation platform. The advantages include its no-code interface, seamless integration with accounting software like QuickBooks or Xero, and its open-source affordability. However, the chart also highlights key limitations such as integration challenges, the need for technical expertise, and data security risks, particularly regarding compliance with regulations like GDPR. The positive impacts of automation are then shown, including reduced manual errors, improved financial decision-making, and time savings for strategic tasks. The flowchart also acknowledges workforce implications, such as the shift from routine tasks to higher-value roles and the need for employee reskilling. It concludes by emphasizing that while n8n offers significant benefits for small enterprises, successful implementation depends on technical support and robust security practices.
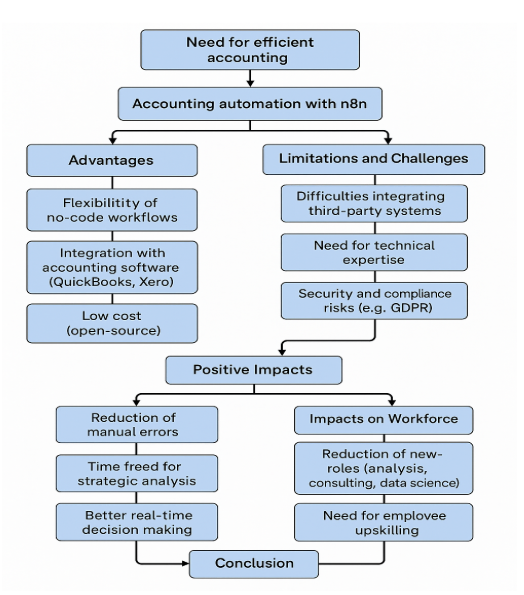
Source: Created by author.
In conclusion, n8n presents a promising solution for small businesses seeking to automate their accounting processes. Its cost-effectiveness, customization capabilities, and potential for streamlining workflows make it an attractive option for businesses with limited resources. However, the challenges related to integrations, data security, and regulatory compliance must be carefully managed. By implementing n8n with proper technical support and ensuring robust security measures, small businesses can significantly improve their accounting operations, reduce errors, and enhance overall efficiency.
References
Brynjolfsson, E., & McAfee, A. (2014). The Second Machine Age: Work, Progress, and Prosperity in a Time of Brilliant Technologies. W.W. Norton & Company.
Chui, M., Manyika, J., & Miremadi, M. (2017). The case for digital reinvention. McKinsey & Company.
Hahn, S., & Kim, S. (2020). The Role of Open-Source Software in Business Automation: Insights from Accounting Technology. International Journal of Accounting and Financial Reporting, 10(1), 42-55.
Jain, V., & Gupta, R. (2019). Automating Accounting with Integrated Systems: An Evaluation of Workflow Tools. Journal of Information Systems, 34(2), 22-37.
Schwab, K., et al. (2018). The Fourth Industrial Revolution. Crown Publishing Group.
Silva, J. F. (2024). SENSORY-FOCUSED FOOTWEAR DESIGN: MERGING ART AND WELL-BEING FOR INDIVIDUALS WITH AUTISM. International Seven Journal of Multidisciplinary, 1(1). https://doi.org/10.56238/isevmjv1n1-016
Silva, J. F. (2024). SENSORY-FOCUSED FOOTWEAR DESIGN: MERGING ART AND WELL-BEING FOR INDIVIDUALS WITH AUTISM. International Seven Journal of Multidisciplinary, 1(1). https://doi.org/10.56238/isevmjv1n1-016
Silva, J. F. (2024). Enhancing cybersecurity: A comprehensive approach to addressing the growing threat of cybercrime. Revista Sistemática, 14(5), 1199–1203. https://doi.org/10.56238/rcsv14n5-009
Venturini, R. E. (2025). Technological innovations in agriculture: the application of Blockchain and Artificial Intelligence for grain traceability and protection. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(3), e78100. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n3-007
Turatti, R. C. (2025). Application of artificial intelligence in forecasting consumer behavior and trends in E-commerce. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(3), e78442. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n3-039
Garcia, A. G. (2025). The impact of sustainable practices on employee well-being and organizational success. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(3), e78599. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n3-054
Filho, W. L. R. (2025). The Role of Zero Trust Architecture in Modern Cybersecurity: Integration with IAM and Emerging Technologies. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(1), e76836. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n1-060
Antonio, S. L. (2025). Technological innovations and geomechanical challenges in Midland Basin Drilling. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(3), e78097. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n3-005
Moreira, C. A. (2025). Digital monitoring of heavy equipment: advancing cost optimization and operational efficiency. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(2),e77294. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n2-011 Brazilian Journal of Development, Curitiba, v.9, n.6, p. 18723-18728, jun., 2023
Delci, C. A. M. (2025). THE EFFECTIVENESS OF LAST PLANNER SYSTEM (LPS) IN INFRASTRUCTURE PROJECT MANAGEMENT. RevistaSistemática, 15(2), 133–139. https://doi.org/10.56238/rcsv15n2-009
SANTOS,Hugo;PESSOA,EliomarGotardi.Impactsofdigitalizationontheefficiencyandqualityofpublicservices:Acomprehensiveanalysis.LUMENETVIRTUS,[S.l.],v.15,n.40,p.44094414,2024.DOI:10.56238/levv15n40024.Disponívelem:https://periodicos.newsciencepubl.com/LEV/article/view/452.Acessoem:25jan.2025.
Freitas,G.B.,Rabelo,E.M.,&Pessoa,E.G.(2023).Projetomodularcomreaproveitamentodecontainermaritimo.BrazilianJournalofDevelopment,9(10),28303–28339.https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv9n10057
Freitas,G.B.,Rabelo,E.M.,&Pessoa,E.G.(2023).Projetomodularcomreaproveitamentodecontainermaritimo.BrazilianJournalofDevelopment,9(10),28303–28339.https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv9n10057
Pessoa,E.G.,Feitosa,L.M.,ePadua,V.P.,&Pereira,A.G.(2023).EstudodosrecalquesprimáriosemumaterroexecutadosobreaargilamoledoSarapuí.BrazilianJournalofDevelopment,9(10),28352–28375.https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv9n10059
PESSOA,E.G.;FEITOSA,L.M.;PEREIRA,A.G.;EPADUA,V.P.Efeitosdeespéciesdealnaeficiênciadecoagulação,Alresidualepropriedadedosflocosnotratamentodeáguassuperficiais.BrazilianJournalofHealthReview,[S.l.],v.6,n.5,p.2481424826,2023.DOI:10.34119/bjhrv6n5523.Disponívelem:https://ojs.brazilianjournals.com.br/ojs/index.php/BJHR/article/view/63890.Acessoem:25jan.2025.
SANTOS,Hugo;PESSOA,EliomarGotardi.Impactsofdigitalizationontheefficiencyandqualityofpublicservices:Acomprehensiveanalysis.LUMENETVIRTUS,[S.l.],v.15,n.40,p.44094414,2024.DOI:10.56238/levv15n40024.Disponívelem:https://periodicos.newsciencepubl.com/LEV/article/view/452.Acessoem:25jan.2025.
Filho, W. L. R. (2025). The Role of Zero Trust Architecture in Modern Cybersecurity: Integration with IAM and Emerging Technologies. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(1), e76836. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n1-060
Oliveira, C. E. C. de. (2025). Gentrification, urban revitalization, and social equity: challenges and solutions. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(2), e77293. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n2-010
Pessoa, E. G. (2024). Pavimentos permeáveis uma solução sustentável. Revista Sistemática, 14(3), 594–599. https://doi.org/10.56238/rcsv14n3-012
Filho, W. L. R. (2025). THE ROLE OF AI IN ENHANCING IDENTITY AND ACCESS MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS. International Seven Journal of Multidisciplinary, 1(2). https://doi.org/10.56238/isevmjv1n2-011
Antonio, S. L. (2025). Technological innovations and geomechanical challenges in Midland Basin Drilling. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(3), e78097. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n3-005
Pessoa, E. G. (2024). Pavimentos permeáveis uma solução sustentável. Revista Sistemática, 14(3), 594–599. https://doi.org/10.56238/rcsv14n3-012
Pessoa, E. G. (2024). Pavimentos permeáveis uma solução sustentável. Revista Sistemática, 14(3), 594–599. https://doi.org/10.56238/rcsv14n3-012
Eliomar Gotardi Pessoa, & Coautora: Glaucia Brandão Freitas. (2022). ANÁLISE DE CUSTO DE PAVIMENTOS PERMEÁVEIS EM BLOCO DE CONCRETO UTILIZANDO BIM (BUILDING INFORMATION MODELING). Revistaft, 26(111), 86. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10022486
Eliomar Gotardi Pessoa, Gabriel Seixas Pinto Azevedo Benittez, Nathalia Pizzol de Oliveira, & Vitor Borges Ferreira Leite. (2022). ANÁLISE COMPARATIVA ENTRE RESULTADOS EXPERIMENTAIS E TEÓRICOS DE UMA ESTACA COM CARGA HORIZONTAL APLICADA NO TOPO. Revistaft, 27(119), 67. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7626667
Eliomar Gotardi Pessoa, & Coautora: Glaucia Brandão Freitas. (2022). ANÁLISE COMPARATIVA ENTRE RESULTADOS TEÓRICOS DA DEFLEXÃO DE UMA LAJE PLANA COM CARGA DISTRIBUÍDA PELO MÉTODO DE EQUAÇÃO DE DIFERENCIAL DE LAGRANGE POR SÉRIE DE FOURIER DUPLA E MODELAGEM NUMÉRICA PELO SOFTWARE SAP2000. Revistaft, 26(111), 43. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10019943
Pessoa, E. G. (2025). Optimizing helical pile foundations: a comprehensive study on displaced soil volume and group behavior. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(4), e79278. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n4-047
Pessoa, E. G. (2025). Utilizing recycled construction and demolition waste in permeable pavements for sustainable urban infrastructure. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(4), e79277. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n4-046
1Bachelor’s degree in accounting
Federal University of Pernambuco
Endereço: (Recife, Pernambuco e Brasil)
E-mail: liliancham@hotmail.com
