REGISTRO DOI: 10.69849/revistaft/ni10202505231418
Alex Tadeu Benevides
Abstract
Mental skills such as confidence, focus, and resilience are essential components of athletic excellence and can be systematically developed through targeted psychological training. This article examines the pivotal role coaches play in fostering these mental attributes to enhance individual and team performance. Drawing from established theories and empirical studies in sport psychology, it explores strategies that coaches can use to build self-efficacy, improve attentional control, and cultivate resilience. The article also discusses the benefits of integrating mental skills training into routine practice and highlights the value of collaboration between coaches and sport psychology professionals. The findings underscore that mental skills development is not only achievable but fundamental to sustaining high-level performance in competitive sports.
Keywords: mental skills, sport psychology, coaching, athlete development, performance enhancement.
The psychological component of athletic performance has garnered increasing attention in recent decades as sports psychologists and coaches recognize the profound influence mental skills have on athletes’ success. Mental attributes such as confidence, focus, and resilience are not innate traits possessed solely by elite performers; rather, they can be systematically developed and enhanced through targeted training. Coaches play a pivotal role in this process, acting not only as technical instructors but also as psychological facilitators who shape the cognitive and emotional readiness of their athletes.
Confidence, often defined as an individual’s belief in their ability to succeed, is one of the most critical psychological variables associated with high performance. Research by Vealey and Chase (2008) highlights that self-confidence is positively correlated with motivation, persistence, and optimal performance outcomes. Coaches can build this attribute through mastery experiences, positive reinforcement, and modeling. By creating environments that emphasize growth over results and by providing constructive feedback, coaches encourage athletes to interpret challenges as opportunities for learning. This approach is supported by Bandura’s (1997) theory of self-efficacy, which asserts that repeated successful experiences foster a stronger sense of personal capability, thereby reinforcing confidence.
Equally important is the athlete’s ability to focus, particularly in high-pressure situations where distractions abound. Focus refers to the capacity to maintain attentional control and remain task-oriented despite external or internal interference. According to Moran (2012), attentional control can be trained using techniques such as goal-setting, visualization, and mindfulness. Coaches who incorporate mental imagery exercises and pre-performance routines into training regimens help athletes internalize behaviors that enhance concentration. Furthermore, the implementation of attentional cue words and simulation training prepares players for real-game stressors, reinforcing their ability to maintain focus under pressure.
Resilience, defined as the capacity to recover from setbacks and adapt to adversity, is essential in competitive sports where failure is inevitable. Fletcher and Sarkar (2012) found that resilient athletes display a unique psychological profile characterized by positive personality traits, motivation, confidence, focus, and perceived social support. Coaches can contribute to the development of resilience by fostering a supportive team culture that encourages open communication, emphasizes the value of effort, and normalizes setbacks as part of the growth process. Creating scenarios in training that mimic adversity—such as playing under fatigue or simulating high-pressure moments—can prepare athletes for the emotional and physical demands of competition.
The coach-athlete relationship is central to effective mental skill development. Jowett and Cockerill (2003) emphasize the significance of trust, empathy, and mutual respect in fostering environments conducive to psychological growth. Coaches who understand their athletes’ personalities, emotional triggers, and motivational drivers are better positioned to tailor interventions that resonate with the individual. Moreover, a holistic coaching philosophy that integrates psychological skills alongside physical and tactical training ensures that athletes are not only prepared for the rigors of competition but also equipped with tools for long-term development and well-being.
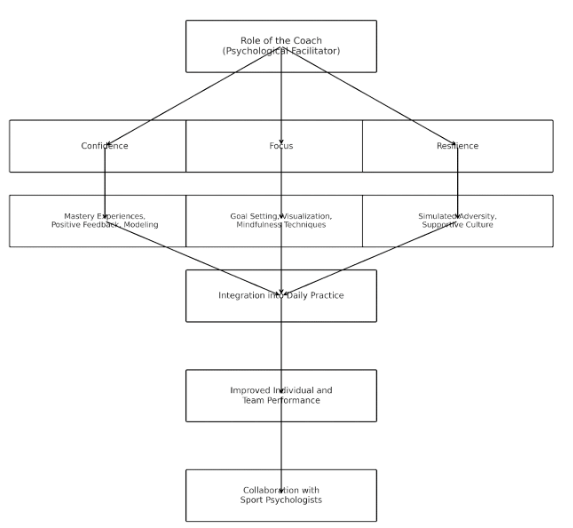
The flowchart titled “Mental Skills Development in Sports Coaching” visually outlines the structured approach through which coaches can foster essential psychological skills in athletes. Beginning with the coach’s role as a psychological facilitator, the diagram branches into three core mental skills—confidence, focus, and resilience—each supported by evidence-based strategies such as mastery experiences, visualization techniques, and exposure to controlled adversity. These elements are then integrated into daily training routines, reinforcing consistency and mental conditioning. The outcome is enhanced individual and team performance, further strengthened through collaboration with sport psychologists. This structured model emphasizes the proactive and strategic nature of mental skills training within competitive sports environments.
Figure 1. Mental Skills Development in Sports Coaching.
Incorporating mental skills training into daily practice not only enhances individual performance but also strengthens team cohesion and collective efficacy. According to Feltz, Short, and Sullivan (2008), collective efficacy—the shared belief in a group’s ability to perform a task successfully—is closely tied to mental preparedness and is significantly influenced by the coach’s leadership behaviors and communication. When coaches model confidence and foster positive peer interactions, they create a psychologically safe space that allows players to experiment, fail, and learn. This not only elevates individual performance but enhances group dynamics, especially in team sports where synchronized mental engagement is vital for success.
Moreover, the integration of sport psychology professionals into coaching teams has shown to be a highly effective approach in developing athletes’ mental skills. As noted by Weinberg and Gould (2018), mental skills consultants can work alongside coaches to deliver structured psychological training programs tailored to the unique needs of each sport and athlete. Techniques such as cognitive restructuring, progressive relaxation, and mindfulness-based stress reduction have demonstrated empirical success in improving focus and managing performance anxiety. Coaches who collaborate with psychologists or receive formal training in psychological principles are thus better equipped to embed mental training into physical routines, creating a comprehensive, multidimensional approach to athletic development.
In conclusion, confidence, focus, and resilience are not fixed attributes but dynamic skills that can be nurtured through deliberate and systematic interventions. Coaches, through their behaviors, communication, and training methodologies, play a central role in facilitating this psychological growth. By drawing on evidence-based practices from sports psychology, coaches can cultivate mentally robust athletes capable of sustaining high performance across diverse competitive contexts. As the field continues to evolve, the integration of mental skills training into everyday coaching practices will remain a cornerstone of athletic excellence.
References
Bandura, A. (1997). Self-efficacy: The exercise of control. New York: Freeman.
Feltz, D. L., Short, S. E., & Sullivan, P. J. (2008). Self-efficacy in sport. Human Kinetics.
Fletcher, D., & Sarkar, M. (2012). A grounded theory of psychological resilience in Olympic champions. Psychology of Sport and Exercise, 13(5), 669–678.
Jowett, S., & Cockerill, I. M. (2003). Olympic medallists’ perspective of the athlete–coach relationship. Psychology of Sport and Exercise, 4(4), 313–331.
Moran, A. P. (2012). Sport and exercise psychology: A critical introduction (2nd ed.). Routledge.
Vealey, R. S., & Chase, M. A. (2008). Self-confidence in sport: Conceptual and research advances. In T. S. Horn (Ed.), Advances in sport psychology (3rd ed., pp. 65–97). Human Kinetics.
Weinberg, R. S., & Gould, D. (2018). Foundations of sport and exercise psychology (7th ed.). Human Kinetics.
Silva, J. F. (2024). SENSORY-FOCUSED FOOTWEAR DESIGN: MERGING ART AND WELL-BEING FOR INDIVIDUALS WITH AUTISM. International Seven Journal of Multidisciplinary, 1(1). https://doi.org/10.56238/isevmjv1n1-016
Silva, J. F. (2024). SENSORY-FOCUSED FOOTWEAR DESIGN: MERGING ART AND WELL-BEING FOR INDIVIDUALS WITH AUTISM. International Seven Journal of Multidisciplinary, 1(1). https://doi.org/10.56238/isevmjv1n1-016
Silva, J. F. (2024). Enhancing cybersecurity: A comprehensive approach to addressing the growing threat of cybercrime. Revista Sistemática, 14(5), 1199–1203. https://doi.org/10.56238/rcsv14n5-009
Venturini, R. E. (2025). Technological innovations in agriculture: the application of Blockchain and Artificial Intelligence for grain traceability and protection. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(3), e78100. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n3-007
Turatti, R. C. (2025). Application of artificial intelligence in forecasting consumer behavior and trends in E-commerce. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(3), e78442. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n3-039
Garcia, A. G. (2025). The impact of sustainable practices on employee well-being and organizational success. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(3), e78599. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n3-054
Filho, W. L. R. (2025). The Role of Zero Trust Architecture in Modern Cybersecurity: Integration with IAM and Emerging Technologies. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(1), e76836. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n1-060
Antonio, S. L. (2025). Technological innovations and geomechanical challenges in Midland Basin Drilling. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(3), e78097. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n3-005
Moreira, C. A. (2025). Digital monitoring of heavy equipment: advancing cost optimization and operational efficiency. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(2), e77294. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n2-011
Delci, C. A. M. (2025). THE EFFECTIVENESS OF LAST PLANNER SYSTEM (LPS) IN INFRASTRUCTURE PROJECT MANAGEMENT. Revista Sistemática, 15(2), 133–139. https://doi.org/10.56238/rcsv15n2-009
SANTOS,Hugo;PESSOA,EliomarGotardi.Impactsofdigitalizationontheefficiencyandqualityofpublicservices:Acomprehensiveanalysis.LUMENETVIRTUS,[S.l.],v.15,n.40,p.44094414,2024.DOI:10.56238/levv15n40024.Disponívelem:https://periodicos.newsciencepubl.com/LEV/article/view/452.Acessoem:25jan.2025.
Freitas,G.B.,Rabelo,E.M.,&Pessoa,E.G.(2023).Projetomodularcomreaproveitamentodecontainermaritimo.BrazilianJournalofDevelopment,9(10),28303–28339.https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv9n10057
Freitas,G.B.,Rabelo,E.M.,&Pessoa,E.G.(2023).Projetomodularcomreaproveitamentodecontainermaritimo.BrazilianJournalofDevelopment,9(10),28303–28339.https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv9n10057
Pessoa,E.G.,Feitosa,L.M.,ePadua,V.P.,&Pereira,A.G.(2023).EstudodosrecalquesprimáriosemumaterroexecutadosobreaargilamoledoSarapuí.BrazilianJournalofDevelopment,9(10),28352–28375.https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv9n10059
PESSOA,E.G.;FEITOSA,L.M.;PEREIRA,A.G.;EPADUA,V.P.Efeitosdeespéciesdealnaeficiênciadecoagulação,Alresidualepropriedadedosflocosnotratamentodeáguassuperficiais.BrazilianJournalofHealthReview,[S.l.],v.6,n.5,p.2481424826,2023.DOI:10.34119/bjhrv6n5523.Disponívelem:https://ojs.brazilianjournals.com.br/ojs/index.php/BJHR/article/view/63890.Acessoem:25jan.2025.
SANTOS,Hugo;PESSOA,EliomarGotardi.Impactsofdigitalizationontheefficiencyandqualityofpublicservices:Acomprehensiveanalysis.LUMENETVIRTUS,[S.l.],v.15,n.40,p.44094414,2024.DOI:10.56238/levv15n40024.Disponívelem:https://periodicos.newsciencepubl.com/LEV/article/view/452.Acessoem:25jan.2025.
Filho, W. L. R. (2025). The Role of Zero Trust Architecture in Modern Cybersecurity: Integration with IAM and Emerging Technologies. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(1), e76836. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n1-060
Oliveira, C. E. C. de. (2025). Gentrification, urban revitalization, and social equity: challenges and solutions. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(2), e77293. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n2-010
Pessoa, E. G. (2024). Pavimentos permeáveis uma solução sustentável. Revista Sistemática, 14(3), 594–599. https://doi.org/10.56238/rcsv14n3-012
Filho, W. L. R. (2025). THE ROLE OF AI IN ENHANCING IDENTITY AND ACCESS MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS. International Seven Journal of Multidisciplinary, 1(2). https://doi.org/10.56238/isevmjv1n2-011
Antonio, S. L. (2025). Technological innovations and geomechanical challenges in Midland Basin Drilling. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(3), e78097. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n3-005
Pessoa, E. G. (2024). Pavimentos permeáveis uma solução sustentável. Revista Sistemática, 14(3), 594–599. https://doi.org/10.56238/rcsv14n3-012
Pessoa, E. G. (2024). Pavimentos permeáveis uma solução sustentável. Revista Sistemática, 14(3), 594–599. https://doi.org/10.56238/rcsv14n3-012
Eliomar Gotardi Pessoa, & Coautora: Glaucia Brandão Freitas. (2022). ANÁLISE DE CUSTO DE PAVIMENTOS PERMEÁVEIS EM BLOCO DE CONCRETO UTILIZANDO BIM (BUILDING INFORMATION MODELING). Revistaft, 26(111), 86. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10022486
Eliomar Gotardi Pessoa, Gabriel Seixas Pinto Azevedo Benittez, Nathalia Pizzol de Oliveira, & Vitor Borges Ferreira Leite. (2022). ANÁLISE COMPARATIVA ENTRE RESULTADOS EXPERIMENTAIS E TEÓRICOS DE UMA ESTACA COM CARGA HORIZONTAL APLICADA NO TOPO. Revistaft, 27(119), 67. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7626667
Eliomar Gotardi Pessoa, & Coautora: Glaucia Brandão Freitas. (2022). ANÁLISE COMPARATIVA ENTRE RESULTADOS TEÓRICOS DA DEFLEXÃO DE UMA LAJE PLANA COM CARGA DISTRIBUÍDA PELO MÉTODO DE EQUAÇÃO DE DIFERENCIAL DE LAGRANGE POR SÉRIE DE FOURIER DUPLA E MODELAGEM NUMÉRICA PELO SOFTWARE SAP2000. Revistaft, 26(111), 43. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10019943
Pessoa, E. G. (2025). Optimizing helical pile foundations: a comprehensive study on displaced soil volume and group behavior. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(4), e79278. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n4-047
Pessoa, E. G. (2025). Utilizing recycled construction and demolition waste in permeable pavements for sustainable urban infrastructure. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(4), e79277. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n4-046
Testoni, F. O. (2025). Niche accounting firms and the brazilian immigrant community in the U.S.: a study of cultural specialization and inclusive growth. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(5), e79627. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n5-034
Leite, E. T. (2025). The power of strategies in sports marketing sponsorship, licensing, and advertising in action. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(5), e79628. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n5-035
Leite, E. T. (2025). The power of strategies in sports marketing sponsorship, licensing, and advertising in action. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(5), e79628. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n5-035
Silva, J. F. (2025). Desafios e barreiras jurídicas para o acesso à inclusão de crianças autistas em ambientes educacionais e comerciais. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(5), e79489. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n5-011
Silva, J. F. (2025). Desafios e barreiras jurídicas para o acesso à inclusão de crianças autistas em ambientes educacionais e comerciais. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(5), e79489. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n5-011
