REGISTRO DOI: 10.69849/revistaft/ch10202504040744
Elvis Alves de Souza
Abstract
The adoption of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in public administration and organizational administrative processes is driving a significant transformation, improving service quality, optimizing resources, reducing costs, and increasing efficiency. AI automates repetitive tasks and analyzes large volumes of data, enabling more informed decisions and more agile and effective management. In public administration, AI has been fundamental in automating processes, allowing public servants to focus on strategic activities while AI handles mechanical tasks. The use of chatbots and virtual assistants improves interaction with citizens, providing quick and efficient responses, resulting in a more satisfactory experience for the public. Additionally, AI positively impacts decision-making by forecasting trends and anticipating problems, optimizing resources, and enhancing government efficiency. AI has also been applied to corruption prevention, through monitoring financial transactions and identifying suspicious behaviors. Although it brings numerous benefits, its implementation faces challenges such as resistance to change, lack of training, and concerns about data privacy. To overcome these obstacles, it is necessary to invest in training, robust infrastructure, and public policies that ensure data protection and the ethical use of technology. Recent studies highlight AI’s potential to optimize organizational processes and improve resource allocation, as well as emphasize the importance of an ethical approach to its adoption. AI can thus profoundly transform public administration and organizations, promoting more modern and innovative management.
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence, Public Administration, Process Automation, Administrative Efficiency, Corruption Prevention.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has rapidly become a crucial tool in numerous sectors, including public administration, where its integration promises to enhance the quality of services, optimize resource allocation, reduce costs, and improve administrative efficiency. The ability of AI to automate processes stands out as one of its main advantages. By taking over repetitive and low-value tasks such as data processing and document analysis, AI allows public servants to dedicate their time to more strategic responsibilities. This automation not only expedites administrative workflows but also cuts operational expenses by minimizing the need for manual labor in routine functions.
Moreover, AI-driven systems like chatbots and virtual assistants are improving how citizens interact with public services. These technologies are designed to automatically handle inquiries and resolve simple issues, delivering faster and more efficient responses with fewer human resources needed. This leads to enhanced service delivery, offering a more satisfying experience for the public while enabling more effective use of available personnel.
Another significant benefit of AI in public administration is its potential to improve decision-making. By analyzing large sets of data, AI can identify patterns, predict future trends, and provide valuable insights that help public managers create more effective policies. This predictive capability enables governments to address issues proactively, optimize their resources, and respond more quickly to the needs of their citizens.
AI also plays a role in combating corruption, a major concern in public administration. Machine learning algorithms can monitor financial transactions, detecting irregularities and fraudulent activities, which helps maintain transparency and accountability in public spending.
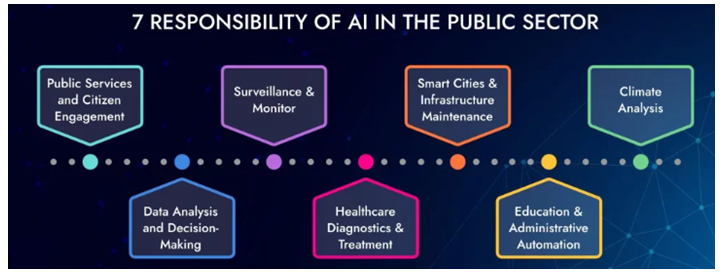
Figure 1: 7 responsibility of AI in the public sector.
Source: ViitorCloud.
Despite its advantages, implementing AI in public administration is not without challenges. Issues such as resistance to change, a lack of adequate training, and concerns about data privacy and security must be addressed. To overcome these barriers, it is essential for governments to invest in staff development, build strong technological infrastructures, and foster a culture of innovation within public institutions.
In conclusion, AI holds tremendous potential to streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve public service delivery. By adopting the right technologies, governments can transform their administrative processes, providing quicker, more accessible, and higher-quality services while ensuring a more efficient use of public resources.
Research by Lu and Gao (2022) highlights AI’s potential in public administration, especially regarding its ability to optimize organizational structures and improve data processing. Their study introduces a management system for public utilities, supported by AI, which enhances work efficiency by reducing redundancy and complexity in administrative tasks. The research underscores AI’s role in improving operational performance and addresses how its data-driven decision-making can resolve management challenges.
Kumar (2024) also examines the transformative effects of AI on administrative functions, focusing on how automation boosts both efficiency and accuracy. The study discusses various AI applications, such as document management, task prioritization, and natural language processing for communication management. Additionally, it explores the role of predictive analytics in improving decision-making and resource allocation. Kumar emphasizes the importance of AI in optimizing administrative workflows and mitigating errors while urging a balanced approach to its ethical implications.
The study by Young, Bullock, and Lecy (2019) explores how AI is shifting public administration from human-driven discretion to “systems-level bureaucracies.” They introduce the concept of “artificial discretion,” which refers to tasks that require decision-making by algorithms. Their analysis suggests that AI can improve efficiency in scalability, cost reduction, and quality enhancement but also raises concerns about equity and the political feasibility of such systems. The authors call for careful consideration of these factors in AI implementation.
Nzobonimpa (2023) revisits key public administration theories to analyze how AI can influence public service delivery. Using task classification models, the study argues that public administration theories provide a solid foundation for integrating AI into service design. Nzobonimpa emphasizes the need for AI systems to be citizen-centered to avoid social biases and improve service outcomes. The study highlights the importance of involving citizens in the design and implementation phases to ensure equitable outcomes.
Engstrom et al. (2020) discuss the transformative role of AI in government agencies, focusing on its potential to reduce costs and enhance decision-making. Their research delves into the design and use of AI algorithms, addressing the balance between human and machine decision-making. Through case studies of leading agencies, the study identifies legal and policy challenges associated with AI adoption and stresses the importance of developing robust frameworks for AI integration in public governance.
Petrova (2023) explores the integration of AI into the management of administrative processes in modern organizations. The research outlines how AI technologies have evolved and identifies the areas where AI is most commonly applied. By reviewing both domestic and international studies, Petrova’s work highlights AI’s ability to streamline administrative functions and improve operational efficiency. The study provides a comprehensive view of AI’s role in organizational management, with a focus on practical applications and the potential for further development within the business environment.
The adoption of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in public administration and organizational administrative processes represents a significant transformation in the way institutions operate, providing not only a substantial improvement in the quality of services offered to the public but also an optimization of resources, cost reduction, and a considerable increase in administrative efficiency. AI capabilities, ranging from the automation of repetitive tasks to the analysis of large volumes of data for more informed decision-making, offer a perspective of modernization that can revolutionize public and business management, making it more agile and effective.
In the context of public administration, AI has proven to be a fundamental tool in process automation, allowing public servants to focus on more strategic tasks while AI takes on mechanical and routine functions. Process automation not only accelerates operations but also reduces operational costs by decreasing the need for a workforce dedicated to repetitive tasks. Furthermore, AI-based systems, such as chatbots and virtual assistants, significantly improve interaction with citizens, providing faster and more efficient responses to their demands without the need for constant human intervention. This results in a more satisfactory experience for the public and a better allocation of human resources.
The use of AI also has a positive impact on decision-making within public administration. With the ability to process and analyze large amounts of data, AI enables the identification of patterns and prediction of trends, offering valuable information that can help public managers implement more effective policies. This predictive capability of AI enables the anticipation of problems, resource optimization, and quicker responses to the population’s needs, contributing to a more efficient and proactive government.
Another relevant benefit of AI in public administration is its application in preventing corruption. Machine learning algorithms can be used to monitor financial transactions, identify suspicious behavior patterns, and detect fraud, which helps promote greater transparency and improve control over public spending. This monitoring and analysis capability can also be applied to enhance the use of resources, optimizing budget allocation and ensuring that public funds are used more efficiently.
However, the implementation of AI in public administration is not without challenges. Resistance to change, lack of adequate training for employees, and concerns about data privacy and security are issues that need to be carefully addressed. To overcome these obstacles, it is essential that governments invest in appropriate training for their staff, develop a robust technological infrastructure, and promote a culture of innovation within public institutions. The creation of public policies that ensure the protection of personal data and transparency in the use of AI is also crucial to ensure that these technologies are applied ethically and responsibly.
Recent studies, such as those by Lu and Gao (2022), Kumar (2024), and Petrova (2023), show that AI has the potential to transform both public and private administration by optimizing organizational processes, improving resource allocation, and enabling more informed decision-making. The research highlights the use of AI in automating administrative tasks, enhancing interaction with citizens, improving operational efficiency, and proactively predicting and solving problems. Additionally, the studies emphasize the importance of an ethical and balanced approach to AI implementation, addressing issues such as equity, transparency, and the legal and political challenges associated with its adoption.
In conclusion, Artificial Intelligence offers immense potential for modernizing public administration and administrative processes within organizations, being a powerful tool to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve the quality of services offered. The adoption of AI-based technologies can profoundly transform the way institutions operate, from automating simple tasks to enhancing strategic decision-making, promoting more efficient use of available resources. However, for these benefits to be fully realized, challenges related to training, infrastructure, data privacy, and security must be addressed. With proper implementation, AI has the potential to redefine the future of public administration and organizations, promoting a more efficient, transparent, and responsive government to the needs of the population, in addition to contributing to a more modern and innovative management in businesses.
References
Engstrom, D., Ho, D., Sharkey, C., & Cuéllar, M. (2020). Government by Algorithm: Artificial Intelligence in Federal Administrative Agencies. LSN: Legal Information & Government (Sub-Topic). https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3551505.
Kumar, D. (2024). AI-driven automation in administrative processes: enhancing efficiency and accuracy. International Journal of Engineering Science and Humanities. https://doi.org/10.62904/qg004437.
Lu, Y., & Gao, X. (2022). The Impact of Artificial Intelligence Technology on Market Public Administration in a Complex Market Environment. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5646234.
Nzobonimpa, S. (2023). Artificial intelligence, task complexity and uncertainty: analyzing the advantages and disadvantages of using algorithms in public service delivery under public administration theories. Digital Transformation and Society. https://doi.org/10.1108/dts-03-2023-0018.
Petrova, E. (2023). Features of implementing AI (artificial intelligence) in the management of administrative processes of a modern organization. Ekonomika i Upravlenie: Problemy, Resheniya. https://doi.org/10.36871/ek.up.p.r.2023.09.04.003.
Young, M., Bullock, J., & Lecy, J. (2019). Artificial Discretion as a Tool of Governance: A Framework for Understanding the Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Public Administration. Perspectives on Public Management and Governance. https://doi.org/10.1093/ppmgov/gvz014.
Venturini, R. E. (2025). Technological innovations in agriculture: the application of Blockchain and Artificial Intelligence for grain traceability and protection. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(3), e78100. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n3-007
Turatti, R. C. (2025). Application of artificial intelligence in forecasting consumer behavior and trends in E-commerce. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(3), e78442. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n3-039
Garcia, A. G. (2025). The impact of sustainable practices on employee well-being and organizational success. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(3), e78599. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n3-054
Filho, W. L. R. (2025). The Role of Zero Trust Architecture in Modern Cybersecurity: Integration with IAM and Emerging Technologies. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(1), e76836. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n1-060
Antonio, S. L. (2025). Technological innovations and geomechanical challenges in Midland Basin Drilling. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(3), e78097. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n3-005
Moreira, C. A. (2025). Digital monitoring of heavy equipment: advancing cost optimization and operational efficiency. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(2), e77294. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n2-011
Delci, C. A. M. (2025). THE EFFECTIVENESS OF LAST PLANNER SYSTEM (LPS) IN INFRASTRUCTURE PROJECT MANAGEMENT. Revista Sistemática, 15(2), 133–139. https://doi.org/10.56238/rcsv15n2-009
SANTOS,Hugo;PESSOA,EliomarGotardi.Impactsofdigitalizationontheefficiencyandqualityofpublicservices:Acomprehensiveanalysis.LUMENETVIRTUS,[S.l.],v.15,n.40,p.44094414,2024.DOI:10.56238/levv15n40024.Disponívelem:https://periodicos.newsciencepubl.com/LEV/article/view/452.Acessoem:25jan.2025.
Freitas,G.B.,Rabelo,E.M.,&Pessoa,E.G.(2023).Projetomodularcomreaproveitamentodecontainermaritimo.BrazilianJournalofDevelopment,9(10),28303–28339.https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv9n10057
Freitas,G.B.,Rabelo,E.M.,&Pessoa,E.G.(2023).Projetomodularcomreaproveitamentodecontainermaritimo.BrazilianJournalofDevelopment,9(10),28303–28339.https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv9n10057
Pessoa,E.G.,Feitosa,L.M.,ePadua,V.P.,&Pereira,A.G.(2023).EstudodosrecalquesprimáriosemumaterroexecutadosobreaargilamoledoSarapuí.BrazilianJournalofDevelopment,9(10),28352–28375.https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv9n10059
PESSOA,E.G.;FEITOSA,L.M.;PEREIRA,A.G.;EPADUA,V.P.Efeitosdeespéciesdealnaeficiênciadecoagulação,Alresidualepropriedadedosflocosnotratamentodeáguassuperficiais.BrazilianJournalofHealthReview,[S.l.],v.6,n.5,p.2481424826,2023.DOI:10.34119/bjhrv6n5523.Disponívelem:https://ojs.brazilianjournals.com.br/ojs/index.php/BJHR/article/view/63890.Acessoem:25jan.2025.
SANTOS,Hugo;PESSOA,EliomarGotardi.Impactsofdigitalizationontheefficiencyandqualityofpublicservices:Acomprehensiveanalysis.LUMENETVIRTUS,[S.l.],v.15,n.40,p.44094414,2024.DOI:10.56238/levv15n40024.Disponívelem:https://periodicos.newsciencepubl.com/LEV/article/view/452.Acessoem:25jan.2025.
Filho, W. L. R. (2025). The Role of Zero Trust Architecture in Modern Cybersecurity: Integration with IAM and Emerging Technologies. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(1), e76836. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n1-060
Oliveira, C. E. C. de. (2025). Gentrification, urban revitalization, and social equity: challenges and solutions. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(2), e77293. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n2-010
Filho, W. L. R. (2025). THE ROLE OF AI IN ENHANCING IDENTITY AND ACCESS MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS. International Seven Journal of Multidisciplinary, 1(2). https://doi.org/10.56238/isevmjv1n2-011
Antonio, S. L. (2025). Technological innovations and geomechanical challenges in Midland Basin Drilling. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(3), e78097. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n3-005
