REGISTRO DOI: 10.69849/revistaft/dt10202212272222
Aline Ferreira Guares Garcia
Abstract
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as an innovative tool in recruitment and talent selection, offering notable benefits such as increased efficiency, cost reduction, and a more impartial and inclusive selection process. AI optimizes repetitive tasks, such as resume screening and profile analysis, allowing recruiters to focus on more strategic decisions, such as assessing interpersonal skills and alignment with organizational culture. By utilizing machine learning algorithms, AI processes large volumes of data quickly, accelerating screening and helping identify promising candidates who might otherwise be overlooked in a manual analysis. Additionally, AI helps reduce human biases in the selection process by minimizing discrimination based on gender, ethnicity, or age, contributing to a fairer and more inclusive hiring process. However, the implementation of AI must be done ethically and transparently, ensuring that algorithms are properly monitored to prevent algorithmic biases that could undermine the fairness of the selection process. While AI optimizes many repetitive tasks, it does not replace human judgment, which remains essential for evaluating factors such as interpersonal skills and cultural fit. By responsibly adopting these technologies, companies can enhance their recruitment and selection processes, finding the most suitable talents for organizational growth and innovation, thereby accelerating their competitiveness in the market.
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence, recruitment, talent selection, impartiality, innovation.
The impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) on talent selection and recruitment has profoundly transformed the way companies attract, select, and hire candidates. As the volume of data increases and the need for more efficient hiring processes intensifies, AI has proven to be a powerful tool for optimizing each stage of the recruitment process, from resume screening to the final interview. One of the main benefits of AI in this context is its ability to analyze large volumes of data in a short amount of time. Through machine learning algorithms, it is possible to scan resumes, cover letters, and candidate profiles for keywords, specific qualifications, and relevant experience for the job at hand. This not only speeds up the screening process but also helps identify talents that could be overlooked in a manual analysis. Furthermore, AI is capable of performing a more precise analysis of candidates’ behavioral profiles and competencies using skills assessment tools and virtual interviews that simulate interactions and gather data on personality and cultural fit.
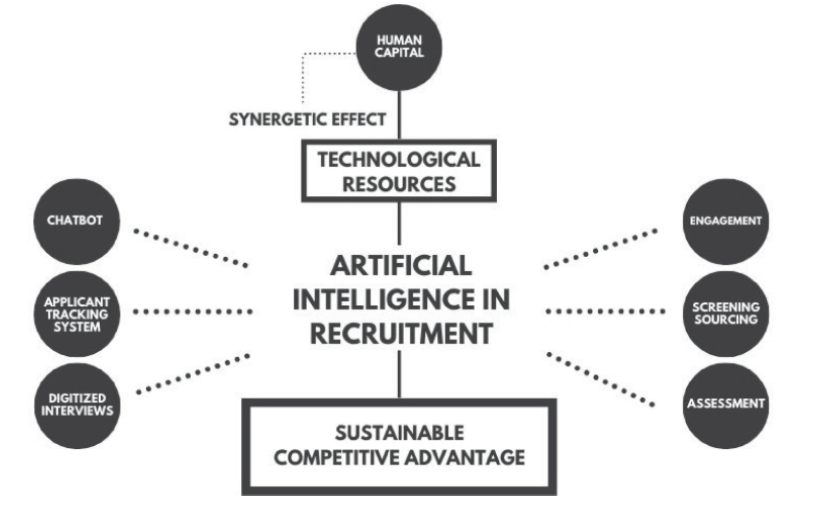
Source: Mehrotra et al. (2022).
Another important aspect of implementing AI in recruitment is the reduction of human biases. Well-trained algorithms can minimize discrimination related to gender, ethnicity, or age, which often affect recruiters’ judgments. By replacing decisions based on subjective perceptions with an objective data analysis, AI contributes to a more inclusive and fair selection process. However, it is crucial to ensure that algorithms are developed ethically and transparently, with proper oversight, to avoid algorithmic biases that may replicate or even amplify existing prejudices. Despite the advantages offered by AI, it does not eliminate the need for human presence. While AI optimizes repetitive processes and provides valuable insights, the recruiter’s critical analysis remains essential for final decision-making, particularly in areas such as interpersonal skills and alignment with organizational culture.
In summary, the adoption of AI in talent recruitment and selection offers various advantages, such as greater efficiency, cost reduction, and more impartial and inclusive processes. However, it is essential for companies to adopt these technologies responsibly, ensuring transparency and ethics at each stage of the hiring process. When implemented correctly, AI can transform recruitment, enabling organizations to find the best talent more quickly and effectively. In this regard, the study by Allal-Chérif, Aránega, and Sánchez (2021) analyzes how digital technologies contribute to improving successive stages of the recruitment process, addressing the concept of e-recruitment as an emerging and multifaceted phenomenon. The study reveals how technologies such as social networks, gamification, and AI are being integrated into recruitment to identify, select, and retain talent, particularly in social enterprises that aim to align candidates’ behaviors and values with the organizational mission.
In turn, the research by Ore and Sposato (2021) explores the opportunities and risks associated with the use of AI in recruitment and selection, from the perspectives of recruitment professionals in a multicultural multinational organization. The results indicate that while AI facilitates the execution of routine tasks through automation, it also generates risks that create apprehension and mistrust among recruiters. Despite concerns about job replacement due to automation, participants believe their roles remain essential, as recruitment should always involve human judgment. This study offers a unique view of the benefits of delegating routine tasks to AI while reaffirming the crucial role of professional recruiters.
In the field of Human Resources, the implementation of AI is also seen as an emerging trend, as highlighted by the study by Hmoud and László (2019). The research explores the impact of AI on optimizing talent acquisition, emphasizing how it can take over repetitive and time-consuming tasks, such as candidate screening, improving the quality of the hiring process and reducing human biases. The study suggests that AI may gradually replace routine administrative functions, being used intelligently to enhance recruitment and selection outcomes. The study by Fraij and Ászló (2021) adopts a systematic review methodology to analyze the impact of AI on Human Resources recruitment processes, identifying the advantages of automating time-consuming tasks, allowing recruiters to focus on more strategic issues. The research highlights that the implementation of AI can provide more efficient, impartial, and rapid data analysis, optimizing the recruitment experience.
Additionally, the study by Acikgoz et al. (2020) investigates how AI affects candidates’ perceptions of fairness during the selection process. The findings reveal that AI-conducted interviews are generally viewed as less fair in terms of procedure and interaction compared to human-led interviews. This suggests that organizations should be cautious when integrating AI, ensuring that perceptions of fairness are taken into account to maintain transparency and attract the best talent. Finally, the study by Manthena (2021) focuses on the application of AI in organizational recruitment, highlighting the benefits of process automation and improved hiring quality, especially when it comes to large-scale recruitment. The study observes that AI has a positive impact on indicators such as time and cost savings, accuracy, bias reduction, increased productivity, and better candidate understanding, emphasizing the importance of HR departments adapting to new technologies to enhance organizational performance.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has established itself as an indispensable tool in recruitment and talent acquisition, transforming the way companies approach the hiring process and, consequently, their organizational outcomes. By bringing efficiency, cost reduction, and a more inclusive approach, AI revolutionizes fundamental aspects of talent attraction. With the exponential increase in available data and the need for more agile and assertive processes, AI presents itself as a strategic solution, enabling recruiters to focus on areas that require human judgment and sensitivity, such as evaluating interpersonal skills and cultural alignment with the organization.
One of the key benefits of this technology is its ability to process large volumes of information quickly and accurately, accelerating resume screening and candidate profile analysis. This results in increased agility in the selection process and allows recruiters to more precisely identify promising candidates who might be overlooked in a manual analysis. At the same time, AI has the potential to drastically reduce human biases, contributing to a more fair and impartial selection process by minimizing discrimination based on gender, ethnicity, age, and other unconscious biases that can influence hiring decisions.
However, it is essential that the implementation of AI is carried out ethically and transparently. The use of algorithms for decision-making carries significant responsibility. Ensuring that these systems are developed and monitored with special attention to the risks of algorithmic bias is crucial to maintaining fairness in the selection process. Therefore, while AI can optimize repetitive processes and provide valuable data, human judgment remains essential, especially for strategic decisions involving interpersonal nuances and cultural alignment—factors that are difficult to quantify through algorithms.
Furthermore, the responsible adoption of these technologies should not only be viewed as a way to improve operational efficiency but also as an investment in a more ethical and inclusive recruitment strategy. By incorporating AI, companies are not just accelerating their operations but also fostering the creation of more diverse and equitable workplaces. This is particularly relevant in an increasingly diverse global landscape, where inclusion and fairness in hiring processes have become a competitive differentiator.
In summary, the integration of AI in recruitment and talent acquisition is not merely a replacement for manual tasks but a transformation that offers numerous advantages. However, like any powerful tool, it needs to be used responsibly. Companies that adopt AI in an ethical and transparent way will be better positioned to attract and retain talent that not only meets the technical requirements of the roles but also aligns with the organization’s values and culture. This will provide a lasting competitive advantage, essential for ongoing success and growth in today’s competitive market.
References
Acikgoz, Y., Davison, K., Compagnone, M., & Laske, M. (2020). Justice Perceptions of Artificial Intelligence in Selection. Decision Making. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijsa.12306.
Allal-Chérif, O., Aránega, A., & Sánchez, R. (2021). Intelligent recruitment: How to identify, select, and retain talents from around the world using artificial intelligence. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 169, 120822. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TECHFORE.2021.120822.
FraiJ, J., & László, V. (2021). A literature review: artificial intelligence impact on the recruitment process. International Journal of Engineering and Management Sciences, 6(1), 108-119.
Hmoud, B., & László, V. (2019). Will Artificial Intelligence Take Over Humanresources Recruitment And Selection. Network Intelligence Studies, 21-30.
Manthena, S. (2021). Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Recruitment and its Benefits. International Journal of Innovative Research in Engineering & Multidisciplinary Physical Sciences. https://doi.org/10.37082/ijirmps.2021.v09si05.013.
Mehrotra, S., & Khanna, A. (2022). Recruitment Through AI in Selected Indian Companies. Metamorphosis, 21(1), 31-39. https://doi.org/10.1177/09726225211066220.
Ore, O., & Sposato, M. (2021). Opportunities and risks of artificial intelligence in recruitment and selection. International Journal of Organizational Analysis. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOA-07-2020-2291.
