REGISTRO DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.11226743
Maria Rismaria Lima Silva Camargo1
ABSTRACT:
This paper examines the impact of rising inflation and interest rates on insurance agencies in the United States, focusing on life, health, and auto insurance sectors. The surge in inflation levels, particularly following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, has prompted significant economic repercussions, prompting the Federal Reserve to implement interest rate hikes to curb inflationary pressures. These macroeconomic shifts have multifaceted effects on insurance agencies, influencing investment income, policy pricing, and coverage costs.
In the life insurance sector, higher interest rates can boost investment returns but may also affect demand for long-term bonds, impacting overall portfolio returns. Rising medical costs and prescription drug expenses directly affect health insurance premiums, while increased investment returns may offset rising costs. Auto insurance faces challenges with inflated repair and medical service costs, potentially increasing claim expenses.
Navigating these challenges requires prudent risk management and strategic pricing decisions to maintain profitability and ensure continued coverage for policyholders. Understanding the nuanced impacts of inflation and interest rate fluctuations on insurance agencies is essential for stakeholders to adapt and thrive in an evolving economic landscape.
Keywords: Inflation, Interest Rates, Insurance Agencies, Life Insurance, Health Insurance, Auto Insurance, Economic Impact, Risk Management, Policy Pricing, Coverage Costs, Federal Reserve.
Current macroeconomic conditions in the U.S.
Inflation has been steadily rising since mid-2021, and after Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, inflation levels started soaring across the U.S., the UK and Europe. In June 2022, the U.S. Consumer Prices Index reached 40-year highs, rising by 9.1%.
Rising levels of inflation equate to rising prices of essential consumer goods and services such as food and fuel and erode people and companies’ purchasing power.
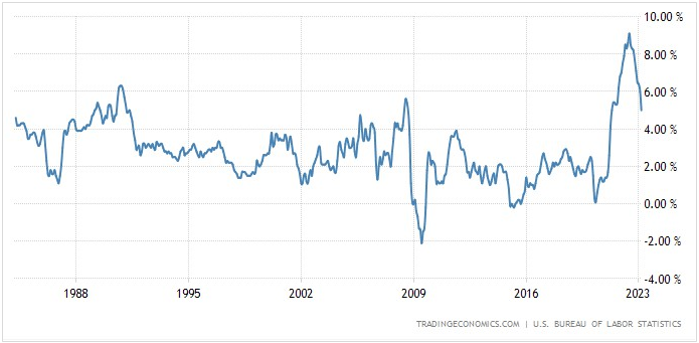
U.S. Inflation rate 1984 – 2023, Source: Trading economics I U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics
In an attempt to stop inflation from rising higher, the U.S. Federal Reserve has introduced a series of interest rate hikes, making the reference rate go from just about zero at the end of the first quarter of 2022 to 5.25 % in May 2023. Interest rates are now at their highest level since late 2007.
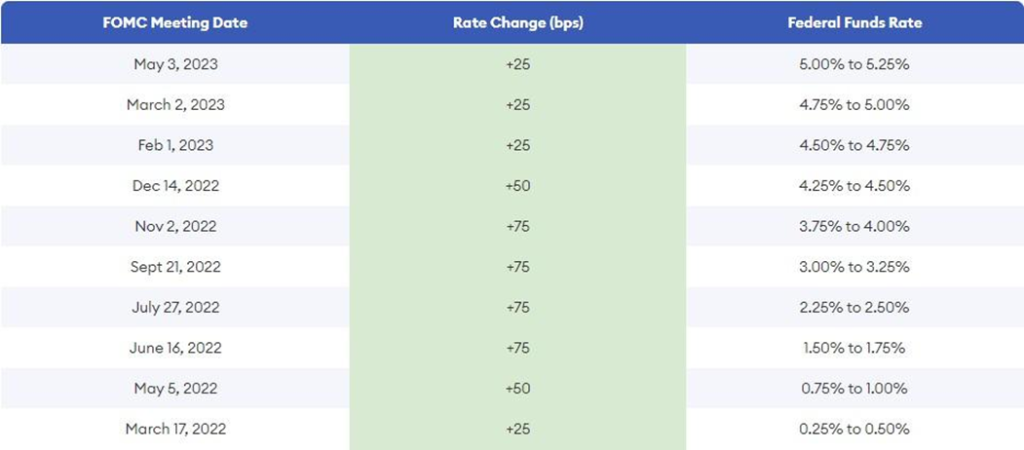
Federal Funds Rate 2022 and 2023 hikes, Source: Forbes
At the May press conference after the FOMC meeting, FED Chair Jeremy Powell once again stated that FED is fully committed to bringing inflation back down to the 2% goal, as price stability serves as the bedrock of every economy. Without price stability, there cannot be a sustained period of strong labor market conditions that benefit all U.S. citizens.
The U.S. economy has slowed significantly from the 2021 rapid pace. The first three quarters saw modest growth rates whereas the U.S. GDP expanded only 0.90% in the fourth quarter of 2022 over the same quarter of the previous year. Growth in consumer spending has slowed in part reflecting lower real disposable income and tighter financial conditions. Activity in the housing sector has weakened significantly, largely reflecting higher mortgage rates. Higher interest rates and slower output growth also impacted businesses’ fixed investments. However, despite elevated inflation, longer-term inflation expectations appear to remain well anchored.
According to the IMF’s World economic outlook from April 2022, growth in the United States is projected to decline from 2.1% in 2022 to 1.6% in 2023 and 1.1% in 2024. Declining real disposable income continues to eat into consumer demand, and higher interest rates are taking an important toll on spending. Inflation is expected to slow down to around 4.5% in 2023 and come near the 2% target in 2024, whereas unemployment is expected to have a slight uptick to around 4.9% in 2024 as inflation slows down.
The FED’s current monetary policy stance, aimed at bringing down inflation, will put business owners and individuals across the country in a very unfavorable lending and spending position.
Impact of current macroeconomic conditions in the U.S. on insurance agencies (life, health and auto insurance)
As the inflation rate in the U.S. hit levels not seen since the 1980s, the Federal Funds Rate has been hiked multiple times resulting in the overall rise of market interest rates. These movements have significant impacts when it comes to the U.S. insurance industry. Overall, the impact of rising inflation and interest rates on U.S. insurance agencies can be complex and multifaceted.
These macroeconomic factors can affect investment income, policy pricing, and the cost of providing insurance coverage. As a result, insurance companies must carefully navigate these challenges to maintain profitability and continue providing coverage to their customers.
Life insurance
Life insurance companies invest the premiums they collect to generate returns, which are used to fund policy benefits and operational expenses. As interest rates rise, the returns on these investments increase, which could benefit life insurance companies in the short term. However, higher interest rates may also lead to decreased demand for long- term bonds, which can reduce the overall returns on life insurance companies’ investment portfolios.
Moreover, rising inflation often leads to increased costs for goods and services. As a result, life insurance companies may need to adjust policy premiums to cover the increased cost of providing benefits.
This could lead to higher policy premiums for new customers and adjustments to existing policies, potentially impacting policy sales and customer retention.
Health insurance
Inflation directly impacts the cost of medical services and prescription drugs, which are key components of health insurance. As medical costs rise, health insurance companies may need to increase premiums to cover these increased expenses.
Also, rising interest rates can impact the profitability of health insurance companies. As investment returns increase, companies may be able to offset rising medical costs without significantly raising premiums. However, this can be a delicate balance, as too much reliance on investment income can create financial instability if interest rates fluctuate.
Auto insurance
Inflation can lead to increased costs for auto repairs, replacement parts, and medical services related to accidents. As a result, auto insurance companies may experience higher claim costs, which could lead to increased premiums for policyholders.
Rising interest rates may impact auto insurance companies’ investment income. Higher investment returns can help offset increased claim costs, potentially reducing the need for premium increases. However, if interest rates rise too rapidly, it could lead to decreased demand for auto loans, which may reduce the overall number of insured vehicles and impact premium revenue.
1 – Sample Market Analysis
1.1 – Location-based Analysis
According to SizeUp4, Insurance Agencies in Orlando, Florida, which will represent Camargo Lima Insurance LLC’s headquarter location and market base, have average annual revenues per establishment in the industry of $2,255,970, which is well above the national average of $1,865,048 and also above the state of Florida’s average of $2,025,274.
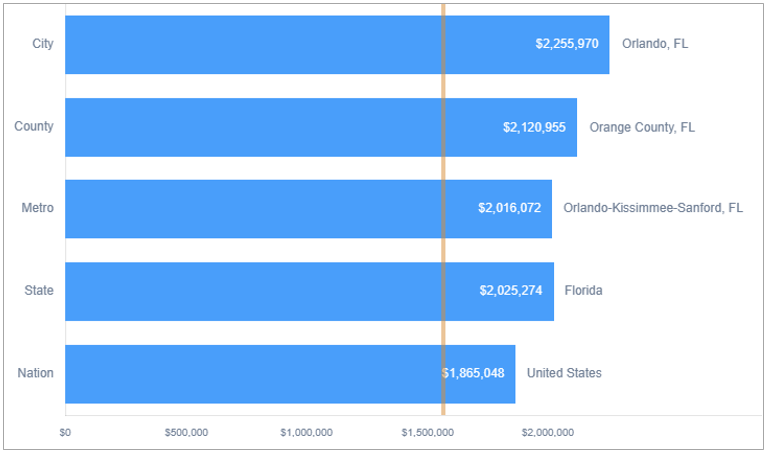
Considerations – Average revenue data for communities on SizeUp is aggregated from data on individual businesses, which comes from hundreds of data sources including, but not limited to, IRS records, county courthouse filings, business publications, and corporate annual reports.
Average annual revenue measures the income that the average business in the area generates from selling its goods and services.
The map shows the areas with the highest average revenue for businesses in the named industry. These are areas the Company may want to target a marketing campaign, open a future business location, or research businesses in these locations to evaluate what they are doing well.
As portrayed in the following graph, Camargo Lima Insurance LLC will be located in the city of Orlando within the state of Florida’s Orange County where annual revenues for Insurance Agencies range from $1,000,000 to $2,800,000, as color- marked on the map displayed below.
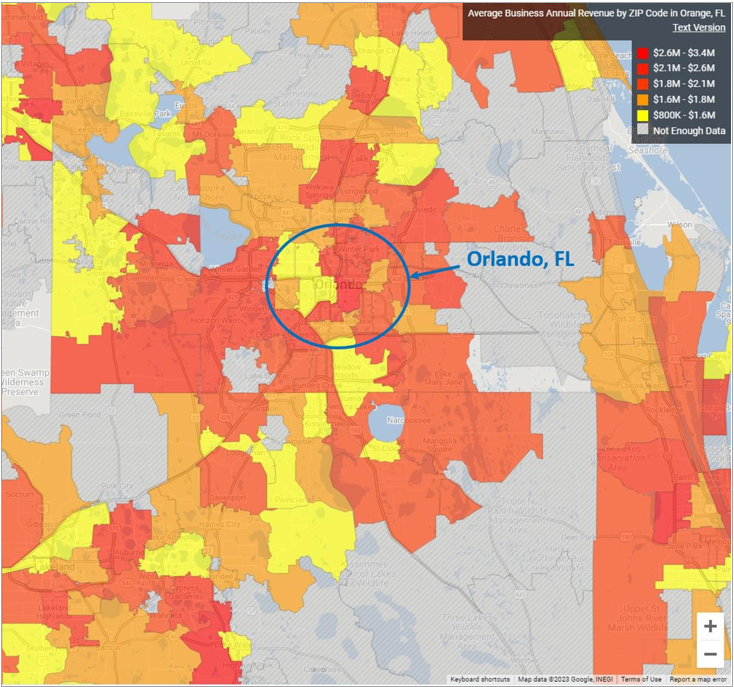
Orlando, FL – range of annual revenues earned by Insurance Agencies
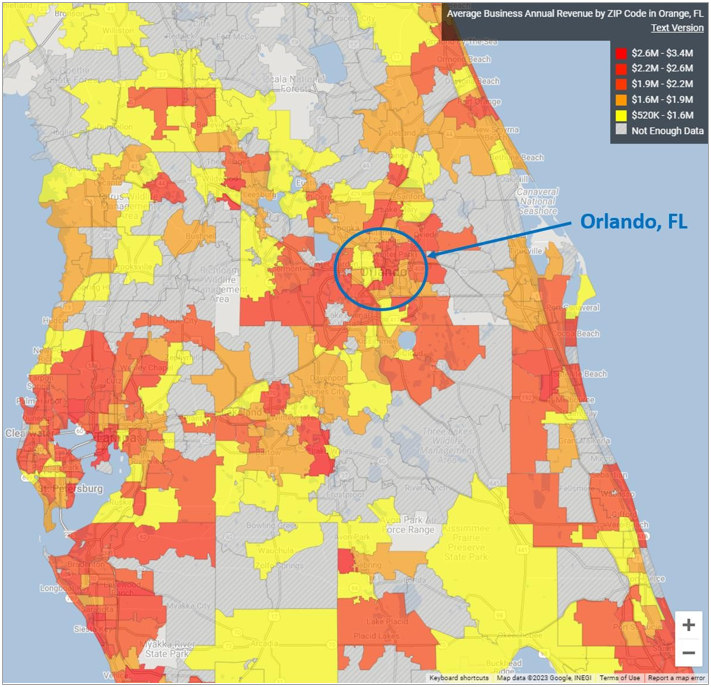
The Company’s locations indicate that regional demand for services provided by Insurance Agencies in Central Florida is strong and steady, which creates an excellent opportunity for the Company to use Ms. Maria Rismaria Lima Silva Camargo’s professional acumen to earn the trust of potential clients in this region.
A prime location, strong industry demand and Ms. Maria Rismaria Lima Silva Camargo’s expertise are expected to enable Camargo Lima Insurance LLC to eventually become an important player in the state of Florida’s insurance market.
➢ 1.2 – Opportunity Zones and HUBZone map
To complement the above displayed, it is also important to highlight that Ms. Maria Rismaria Lima Silva Camargo intends to form a new U.S. Company, generate new employment opportunities and work in and serve the citizens of some of the economically distressed communities also known as Opportunity Zones5, defined by individual census tract, nominated by America’s governors, and certified by the U.S. Secretary of the Treasury via his delegation of that authority to the Internal Revenue Service.
The Opportunity Zones initiative is not a top-down government program from Washington but an incentive to spur private and public investment in America’s underserved communities. Currently, there are 8,764 Opportunity Zones in the United States, and California, Texas, New York, Florida, Illinois and Michigan are among the states with the most opportunity zones.
The state of Florida has 427 designated Opportunity Zones, all of them being low-income communities. Orange County is home to 24 of the 427 Opportunity Zones in Florida, out of which 12 zones fall within the city of Orlando.
In total, Orlando’s Opportunity Zones have a population of approximately 41,000, representing 14% of the inner city’s total population of 290,000. The Median Household Income in Orlando, FL, is $36,000 and the median age is 38 years while 26% of the citizens of the city’s 12 Opportunity Zones are considered as living below poverty line.

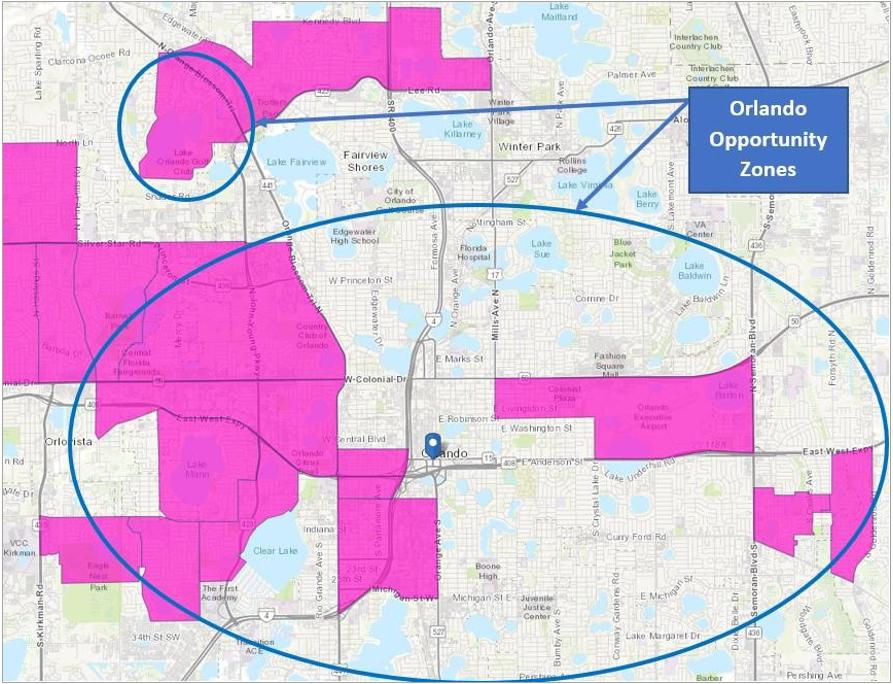
The city of Orlando, FL – colored areas in and surrounding the city recognized as Opportunity Zones
Ms. Maria Rismaria Lima Silva Camargo’s proposed professional endeavor also aligns with the locations of some of the underprivileged areas and communities that have high poverty rates and are considered to be in the Historically Underutilized Zones (HUBZone)6 in accordance with the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) agency’s HUBZone program and the following map that displays diverse areas in and around of the city of Orlando, FL which are designated as HUBZone Qualified Census Tracts.
HUBZone Qualified Census Tracts are designated by the Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) based on high poverty and low household income criteria.
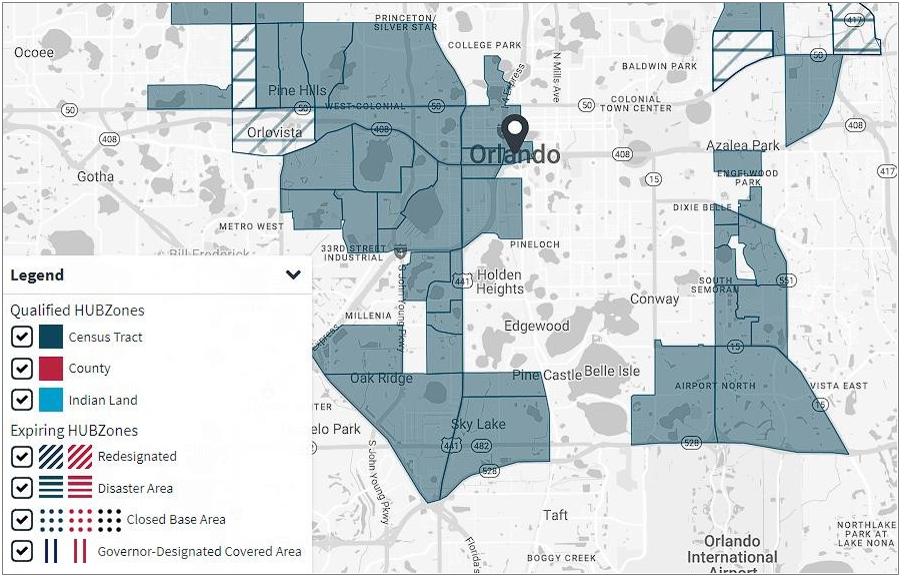
The city of Orlando, FL – areas in and surrounding the city designated as qualified HUBZones
2 – Industry Significance
Insurance Brokers & Agencies in the U.S.
According to IBISWorld, one of the world’s leading publishers of business intelligence specializing in industry and procurement research the Insurance Brokers & Agencies7 industry includes individuals and businesses that primarily act as agents or brokers in selling insurance policies and annuities. Industry participants earn commission income, mostly as a percentage of the premium of insurance policies sold. They also earn some fee income for providing risk management consulting and other value-added services.
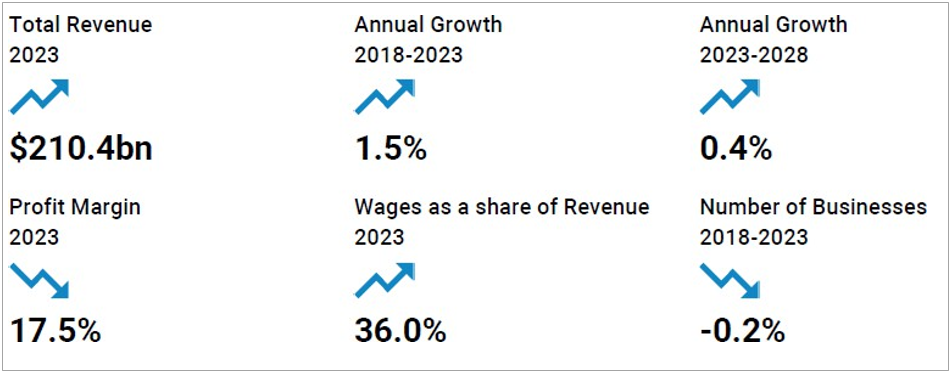


➢ Current Performance
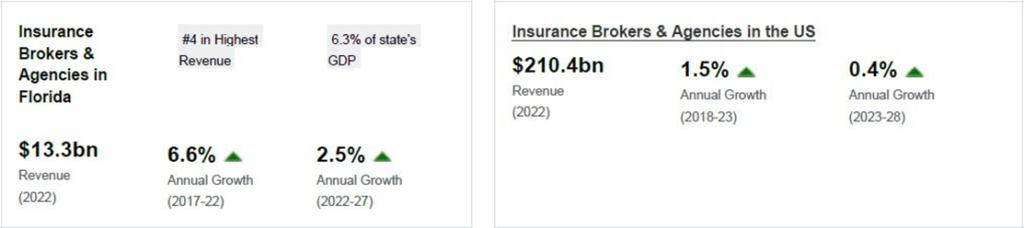
The Insurance Brokers and Agencies industry endured 1.5% revenue growth to $210.4 billion over the past five years, including an estimated 0.1% increase in 2023 when the profit margin is anticipated to reach 17.5%.
Hardening cycle ensures industry resilience, leads to growth
° The industry is heavily dependent on macroeconomic conditions that determine how prices for insurance policies will fluctuate for consumers and businesses alike.
° When the industry is in a hardening cycle, prices set by insurance providers increase, while a softening price cycle means prices will go down. The prices are set in response to macroeconomic conditions; for example, a region that has a higher rate of natural disasters will often see higher prices on homeowners’ insurance.
° Two sectors that have experienced this trend are health and P&C (Personal and Casualty) insurance markets due to an aging population and a higher risk of natural disasters.
COVID-19 produces mixed results for industry
° Although the COVID-19 pandemic harmed consumer demand in certain niches of the industry, the effect on revenue growth was relatively minimal. Since the industry touches multiple influential sectors like healthcare and homeownership, the effect of the pandemic shifted consumer demand toward other insurance categories.
° Economic volatility in 2020 caused declines in the number of people with private health insurance; however, the homeownership rate jumped in that same year as consumers took advantage of a slumping housing market, which shifted consumer demand toward that industry niche.
° Employment trends also affected industry growth, with heightened unemployment in 2020 causing consumers to shift toward alternative forms of insurance through government-funded programs like Medicaid.
Increased industry competition is shifting the broader business model
° The growth of online servicing of insurance policies and external competitors such as banks and consulting firms have resulted in an evolution of the traditional business model.
° With competition particularly high after the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the broader economy, major insurance firms such as Liberty Mutual Group shifted resources toward their sales and marketing departments to improve their DTC (direct-to consumer) outreach. The addition of mobile apps and expansion of online advertising via TV ads by companies like GEICO further highlight this evolving business model.
° The insurance brokers and representatives have also faced change, with more emphasis being placed on risk management and consultation skills to effectively capture a broader share of the consumer base.
Larger necessity for interpretation of insurance policies has bolstered industry participation
° With many recent changes in major industry markets such as healthcare, demand for workers to assist consumers in understanding the policies on the marketplace remained resilient.
° Despite the COVID-19 pandemic shifting consumer demand toward different industry niches, the constant necessity for consumers to better understand their insurance policy led insurance brokers and agencies to expand their workforce to provide a high level of customer satisfaction.
° For example, the complexities of insurance policies following the passage of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA) led insurance brokers to expand their customer outreach to improve customer satisfaction.
➢ Industry Outlook
The Insurance Brokers and Agencies industry is anticipated to experience revenue growing an annualized 0.4% to $214.7 billion over the next five years, with profit set to reach a 17.5% margin in 2028.
Strong macroeconomic growth set to ensure industry growth
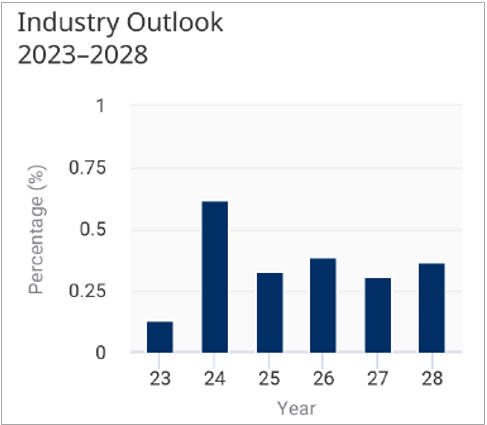
° With the worst of the COVID-19 pandemic in the rearview mirror, the industry is set to benefit from macroeconomic growth in multiple areas. The increase in per capita disposable income, coupled with a rebound in the business confidence index over the next five years, bodes well for industry demand.
° Since the industry is heavily dependent on positive economic sentiment among consumers, the developments in these indicators are set to fuel further industry revenue growth over the next five years.
° This growth may change in terms of the different insurance policies consumers purchase, with a shift in demand from homeowners’ insurance toward health insurance and vehicle insurance.
Shifting sales trends following COVID-19 pandemic will boost profitability, lower marginal costs
° The use of technology as an accelerant for online sales and expanding DTC capabilities is poised to strengthen industry growth.
° With the COVID-19 pandemic changing how the majority of consumers sign up for new insurance policies, the growth of online capabilities and an online presence bodes well for industry operators that look poised to benefit from this trend.
° Although online sales are beneficial for lower labor intensity for employees in the industry, the presence of in-person offices for larger customers like corporations highlight the balance operators will look to strike in the coming years.
Change in demand of the type of insurance coverage will contribute toward steady revenue growth
° As consumers adapt fiscally following the COVID-19 pandemic, the types of insurance coverage in demand will change as well.
° The pent-up demand for consumers to travel will have a notable impact on how in-demand vehicle insurance will be, particularly for new vehicles as a result of strong per capita disposable income growth over the next five years.
° Life and health insurance will be two other sectors that will benefit from this demand, as people will want a safety buffer for themselves and their loved ones as travel and socializing rates increase.
Businesses rebounding will translate to a consistent stream of potential customers
° With businesses having been hit the hardest during the COVID-19 pandemic, the renewed positive trend for business sentiment is a sign of positive industry growth in the near future.
° Since businesses require significantly more insurance policies, which translates to larger operational costs, the broader industry is poised to capture this demand, especially as businesses recover due to an influx of stimulus spending through programs such as the Paycheck Protection Program (PPP).
Barriers to Entry in this industry are Medium and the trend is Increasing.
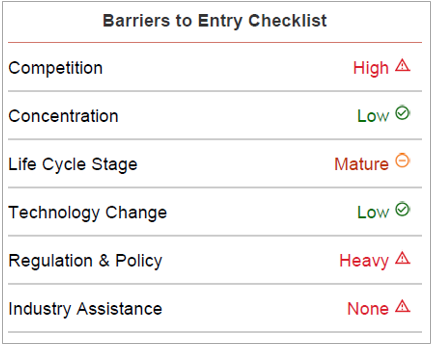
The legal barriers within the industry are notable and have an effect on how successful a new entrant will be. In addition to a competitive marketplace, entrants must comply with strict regulations from the government and follow high ethical standards.
There are no unique start-up costs necessary for a new entrant. Some of the biggest initial expenses involve rent and other capital expenses of the physical locations themselves, with acquisition of the necessary technology also a key cost procured initially of customers and maintain a steady profit margin.
However, the level of competition is high within the industry, as industry operators look to secure the best price point within the markets, they serve to accumulate the most consistent stream
Capital Intensity Insurance Brokers and Agencies face large amounts of capital costs in the form of start-up costs. As the industry firm matures over time, maintenance of existing locations coupled with acquiring more efficient technology adds to the capital intensity.
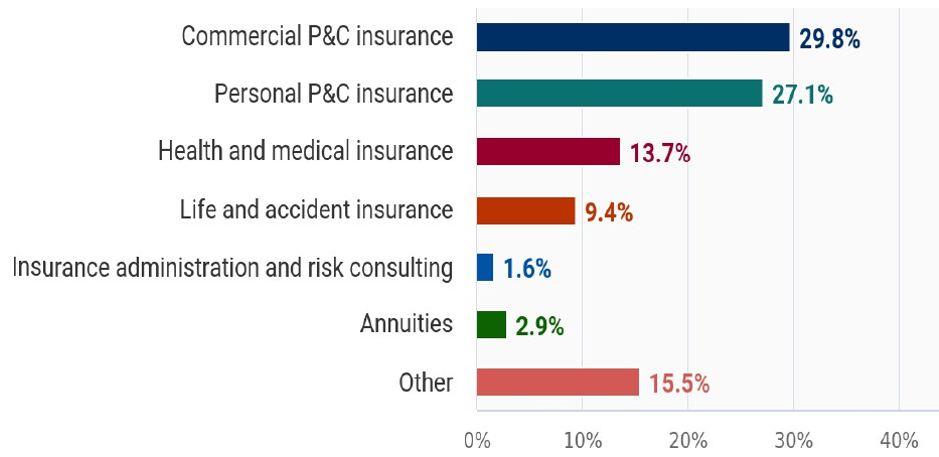
➢ Products and Services Segmentation
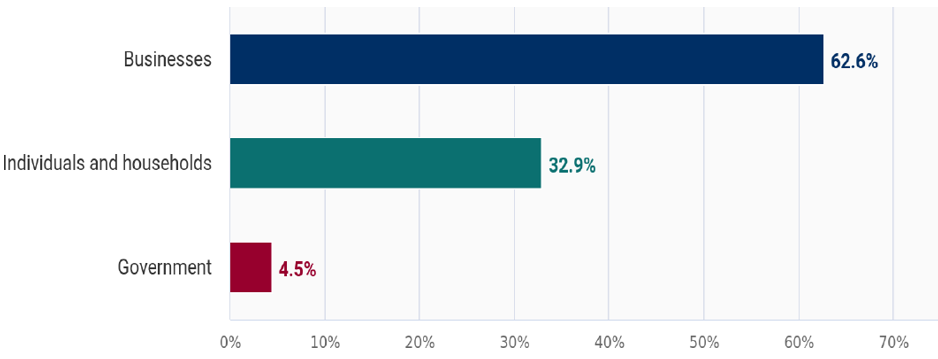
➢ Major Markets
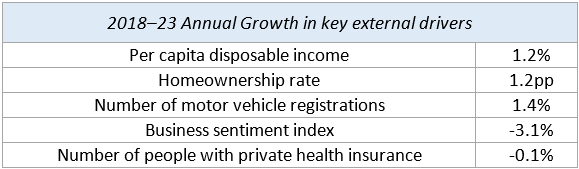
➢ Key External Drivers
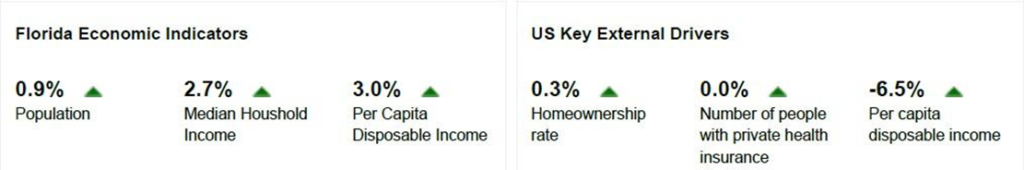
° Homeownership rate – The US homeownership rate influences demand for insurance. While this rate fluctuates on an annual basis, the stock of houses remains relatively constant and most revenue generated by homeowners’ insurance comes from renewals. Still, an increase in the homeownership rate typically translates into higher demand for insurance and therefore, commissions for industry operators. The homeownership rate is expected to increase in 2023.
° Number of people with private health insurance – Brokers play an important part in distributing health insurance policies. For example, a significant portion of small companies, which are those between two and 50 workers, purchase health benefits through agents or brokers. Therefore, an increase in health insurance membership tends to be a boon for agents and brokers.
° Per capita disposable income – An increase in personal disposable income results in higher activity in the insurance market. As peoples’ earnings grow, the need for insurance also expands as they buy cars, homes and other assets that need to be protected. Additionally, higher per capita disposable income enables individuals to expand coverage because they can afford high premiums. This factor is particularly the case for life, property and casualty lines. Per capita disposable income is expected to increase in 2023, representing a potential opportunity to the industry.
° Number of motor vehicle registrations – The number of cars registered influences demand for individual automotive insurance. While automotive sales have little effect on the number of cars on the road, they are an important indicator of policy prices because newer cars are normally costlier to insure. The number of motor vehicle registrations is expected to increase in 2023.
° Business sentiment index – The Business Sentiment Index measures the current mood and economic satisfaction of businesses across the United States. This index takes into account multiple measures like inventory levels, employment rates and supply deliveries, with a higher sentiment associated with a stronger economy. If the index increases, it bodes well for the industry, as it highlights a proactive economy and positive trends within the business world. This indicator is anticipated to decrease in 2023, posing a potential threat to the industry.
➢ Key Success Factors
IBISWorld identifies 250 Key Success Factors for a business, and the most important for the Insurance Brokers & Agencies Industry include:
Having links with suppliers – Agencies and brokerages must establish relationships with underwriters to increase the number of risk products they can offer in retail and wholesale markets.
Having an extensive distribution network -Agencies and brokerages must possess an extensive distribution network to attract both primary underwriters and purchasers of risk products.
Having a good technical knowledge of the product – Having a solid understanding of the products that are distributed will separate the most successful agencies and brokerages from the less successful.
Must comply with government regulations – Insurance agencies and brokerages must comply with state and federal legislation, which affects the entire insurance sector
➢ Business Location
Southeast region ensures top spot
✯ With over a quarter of the population residing in the Southeast, the industry has followed this population trend, as the largest number of industry establishments reside in this region.
✯ Insurance brokers and agencies benefit from highly concentrated areas that have large metropolitan hubs and higher valued properties such as homes.
✯ States such as Florida make up a significant portion of the establishments percentage, with a largely concentrated population coupled with higher risk of natural disasters like hurricanes creating a lucrative market for the industry.

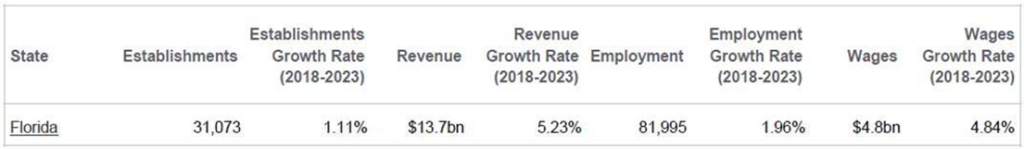
Insurance Brokers & Agencies in Florida8
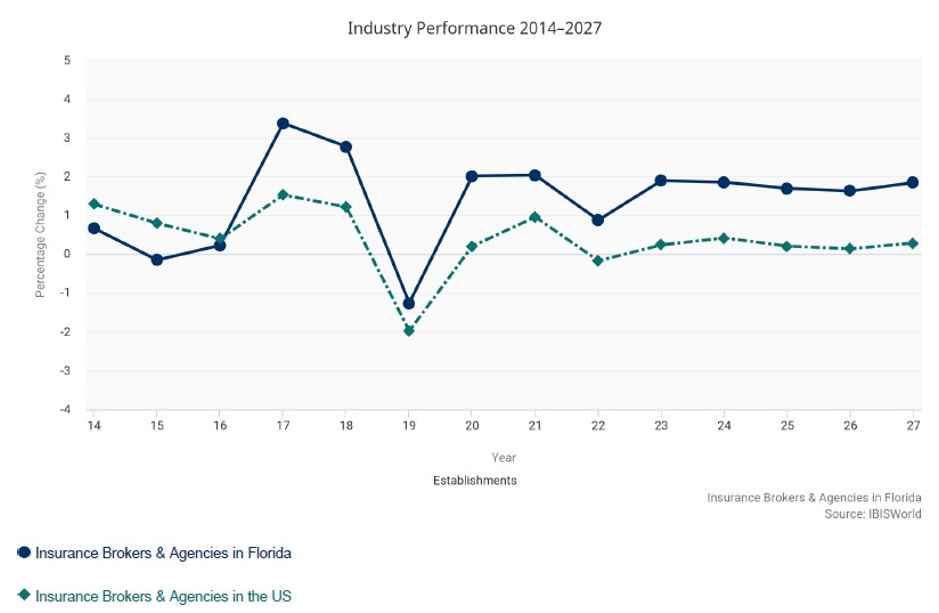
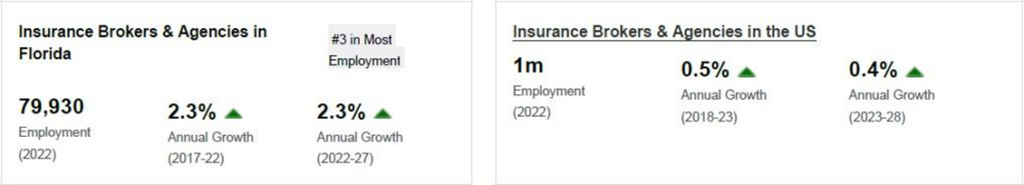
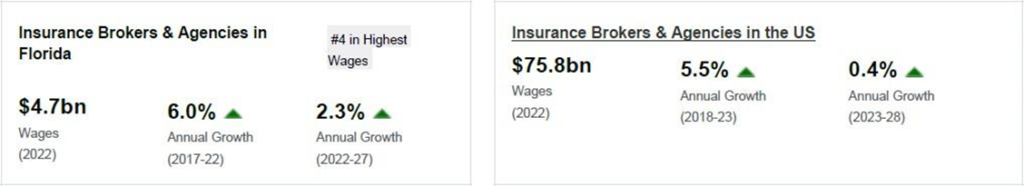
The Insurance Brokers & Agencies industry in Florida has grown at an annualized 6.6% to $13.3 billion over the five years to 2022, while the national industry grew at 1.5% during the same period. Industry establishments increased an annualized 1.3% to 30,493 locations. Industry employment has increased an annualized 2.3% to 79,930 workers, while industry wages have increased an annualized 6% to $4.7 billion.
Over the four years to 2027, the industry is expected to grow an annualized 2.5% to $15.0 billion, while the national industry is expected to grow 0.5%. Industry establishments are forecast to grow 1.8% to 33,319 locations.
Industry employment is expected to increase an annualized 2.3% to 89,367 workers, while industry wages are forecast to increase 2% to $5.2 billion.
Establishments

Revenue
Employment
Wages
Key External Drivers
4https://company.sizeup.com
5https://opportunityzones.hud.gov/resources/map
6https://maps.certify.sba.gov
7Source: IBISWorld, Insurance Brokers & Agencies in the US, January 2023
8Source: IBISWorld, Insurance Brokers & Agencies in Florida, August 2022
