REGISTRO DOI: 10.69849/revistaft/ma10202407190754
Juliana Ribeiro Artur1
Rosana Maria Gasparoti1
Angela Mara Rambo Martini2
Adriane Viapiana Bossa3
ABSTRACT
Medicinal Biomagnetism (MB) is an Integrative and Complementary Practice in Health (PICS – Prática Integrativa e Complementar em Saúde) in Brazil. This therapeutic system was developed by Dr. Isaac Goiz Durán, in 1988. The practice consists of recognizing points with altered energy in the human body. Once the imbalances are identified and the bioenergetic dysfunctions corrected, it adjusts to the pH of the tissues involved and its health is restored. The MB uses Static Magnetic Fields (SMF) for the treatment in a non-invasive and easy to apply way. After more than 30 years of clinical practice, protocols for the treatment of various diseases were created. Uterine Fibroids or Myomas are benign smooth muscle tumors. There is an exaggerated growth of the myometrium cells in a delimited way, giving the myomas the appearance of nodules. The objective of this work is to present a protocol for the treatment and prevention of Uterine Fibroids. The methodology used in this study was a described bibliographic review of a quantitative and exploratory nature of related themes for the selection and presentation of the Uterine Fibroids Protocol. It can be used by health professionals, therapists or people who strive for self-responsibility in care, disease prevention or improvement in quality of life. It was concluded that it is important to continue producing scientific evidence related to the use of MB protocols, without leaving aside the preventive principle proposed by the PICS in Brazil, to simply stimulate self-care and self-management of quality of life.
Keywords: Medicinal Biomagnetism; Biomagnetic Pair; Protocol; Integrative and Complementary Practices; Uterine Myoma; Static Magnetic Fields; Magnets.
1. INTRODUCTION
Uterine myoma is a benign tumor that grows in the muscle tissue of the uterus that affects women mainly during reproductive age. This benign tumor is the most common gynecological malignancy and can cause a variety of health complications. Despite their benign character, myomas are responsible for high morbidity in the female population and represent a public health problem with high costs (BARCELOS et al., 2021).
Myoma is a disease of women in reproductive age and presents a relationship with the hormones, estrogen and progesterone. They are classified by their location in the uterus and cause symptoms that are directly related to the size, number and where they are located, such as abnormal uterine bleeding, pelvic pain, dysmenorrhea and reproductive changes. Intramural fibroids develop within the uterine wall and are more likely to enlarge and distort the uterine cavity. The submucosal fibroids develop from the myometrial cells beneath the endometrium and project into the uterine cavity. The subserosal fibroids originate from the serous surface of the uterus, may have a pedunculated base or extend to the ligaments of the uterus (PAVNA, KRISTINA and CHRISTMAN, 2006).
In recent decades, there has been an increase in demand for forms of health care that differ from conventional standards, seeking an approach to care for the subject in an integral way, covering body, mind and spirit. As a result, the vertical growth in the offer of integrative and/or complementary practices opposed to conventional treatment has been growing a lot, and their indications have stimulated academic discussions around the safe and effective use of these therapeutic modalities (ISER, KRACIK and PEREIRA, 2019).
Integrative Medicine (IM) came to fill the gap in traditional health, which can be described as a set of health practices that combine non-allopathic techniques with modern medicine, which is based on four pillars, namely, treatment of the individual as a whole, and not in a Cartesian manner; non-hierarchical and interdisciplinary relationship with Conventional Allopathic Medicine; multidisciplinary approach and consensus building and; care for effectiveness and affordable cost (ISER, KRACIK and PEREIRA, 2019).
A diversity of practices that are not regulated as medical specialties in Brazil are identified within IM. The recognition of these practices in Brazil, with the increased demand for these services, led, in 2006, to the implementation of the National Policy on Integrative and Complementary Practices (PNPIC – Política Nacional de Práticas Integrativas e Complementares), which standardized and regularized the practice of IM in the country for its use in the Brazilian Public Health System (SUS – Sistema Único de Saúde) (ISER, KRACIK and PEREIRA, 2019).
Added to this, there has been greater popular interest in PICS, whether at the public level in the SUS with the 29 regulated practices in the PNPIC, or at the private level with the hundreds of IM offered to the population. With the high cost of biomedicine, the high potential of IM as a health promoter and generator of well-being, and with the increase in chronic diseases, life expectancy and the search for a better quality of life, IM intensifies the sense and the capacity for self-care, being a fundamental ally in maintaining health (ISER, KRACIK and PEREIRA, 2019).
Medicinal Biomagnetism (MB) is an IM offered in private practice since it has not yet been contemplated by the PNPIC to be offered in the SUS and has been developing as a disease prevention and treatment system since 1988, when Dr. Isaac Goiz Durán, identified that bioenergetic changes in anatomical regions, in energetic and vibrational resonance, could be treated with medium-intensity SMFs. Bioenergetic alterations are called Biomagnetic Pairs (BMPs) in the MB therapeutic system (DURÁN, 2008; BOSSA et al., 2023).
The BMP is the set of dysfunctional bioelectric charges that are related to a pathology. Composed of two main charges of opposite polarity, which are formed due to bioelectromagnetic changes in temperature and pH of tissues or organs. The BMPs are sustained within the organism through the vibrational and energetic resonance between the charges of the biochemical elements involved in the process (DURÁN, 2008; MARTÍNEZ, 2018).
It is specified that the charges are bioelectric and are capable of producing a phenomenon of pelvic limb dysmetria if the magnets are positioned in a specific way on the body. These charges, once balanced (depolarized), stop inducing the phenomenon of pelvic limb dysmetria, and in this sense the SMFs, generated by the therapeutic magnets of the MB, are capable of producing a therapeutic effect of pH balance and recovery of the health state in general (MARTÍNEZ, 2018).
The generation and treatment of BMPs are based on natural laws and elementary principles of physical matter. BMPs form south and north magnetic poles, from the dysfunctional accumulation of charges of H+ in one region, maintaining the south pole of the BMP and OH- or other free radicals maintaining the North pole of the BMP in another anatomical point. It is observed that there are secondary dysfunctions to the processes of magnetic polarization of the internal organs involved, and that, in addition to pH dysfunction, the South pole of the BMP, where the accumulation of positive charges occurs, produces functional metabolic and energetic excitations and, at the pole North, which maintains negative charges, there is a decrease in normal metabolic function (BROERINGMEYER, 1991; DURÁN, 2014).
According to Dr. Isaac Goiz, normal homeostasis in the body is a direct function of acid-base balance. When the pH balance is disturbed it creates an environment conducive to the development of pathogens and the accumulation of harmful substances. Medicinal Biomagnetism (MB) as a complementary health practice, aims to study, detect, classify, measure and correct these bioenergetic disturbances and can also identify, through energy testing, the presence of pathogenic microorganisms such as viruses, bacteria, fungi, parasites and archaea as well as detect glandular and tissue energetic dysfunctions (DURÁN, 2008; BOSSA et al., 2023).
The organism examination to identify BMPs is called Complete Scanning (DURÁN, 2005, 2008 and 2014; MARTÍNEZ, 2018; BOSSA, 2023; CORRÊA et al., 2023), and was also described by Frank (2017). After more than 30 years of MB clinical practice, protocols for the treatment of various diseases were created. Most of the protocols originated from the observational analysis of the BMPs that were most repeated during the Complete Scannings and that were treated during the follow-up of the clinical improvement of the signs and symptoms of the diseases (MARTÍNEZ, 2018). Thus, the objective of this study is to present a MB protocol for the treatment of uterine fibroids that can encourage self-responsibility in the care and improvement in the quality of life of women affected by myomas.
2. METHODOLOGY
A descriptive bibliographical review, of a quantitative nature related to the theme for the selection and presentation of the Protocol for the Treatment of Uterine Myoma was used as a study method. According to Freitas (2017), quantitative research aims to explain the subject of study, generate knowledge, prove theories, arrive at more precise propositions and make specific recommendations applicable to a broader population, so that they serve to the solution of problems or decision-making (FREITAS, 2017).
The search for articles was carried out in the year 2022. The electronic databases platforms Scientific Electronic Library Online (SCielo), Google academic and PubMED were used. Articles in English and Portuguese were included, prioritizing articles with DOI – Digital Object Identifier.
The selection of titles was based on inclusion criteria of articles in English and Portuguese from the last 20 years, available in full and free of charge. Materials that do not address the theme, without DOI and repeated were excluded. The descriptors used for the search were Medicinal Biomagnetism, Uterine Myoma, Integrative Medicine. The Boolean descriptor “AND” was included for Bacteria and Static Magnetic Fields, Myoma and Virus, as well as for Myoma and Papilloma.
Due to the scarcity of material on MB and its protocols on digital platforms, content searches were carried out in books, theses and workshop handouts available in the library of the graduate program in Biomagnetism and Bioenergetic Applied to Health at Par Magnético Institute (IPM).
3. RESULTS
As a result of the methodological search, 127 articles were found with the descriptor Uterine Myoma, 71 in SCIELO, 56 in PubMED, increasing to 26,835 results when the descriptor Uterine Myoma was used. As for the descriptor Integrative Medicine, 336 were found in SCIELO, 146 in PubMED. Exclusion criteria were applied, leaving 3 publications to be used in this study.
Searches with the Boolean descriptor “AND” in Bacteria And Static Magnetic Fields resulted in 135 studies found in PubMED. For the descriptor Myoma and Papilloma, 22 results were found in PubMED. For the descriptor Myoma and Virus, 29 results were found. After applying the exclusion criteria, 2 articles remained for this study.
Regarding the search for works on the theme of Medicinal Biomagnetism, works published in journals and magazines are scarce. For this reason, 10 articles were identified, 4 with DOI and related to the theme were used as a reference for this study; 13 MB books were also selected and used as well as 7 handouts from courses on the technique from which 2 remained. The total of 15 works on MB were referenced in this study.
Based on the above, a total of 19 references formed the basis of the bibliographic references that were used in the descriptions of uterine fibroids and MB in general. In the existing literature in the specific area of MB, the Protocol for the Treatment of Uterine Myoma (PTUM) was identified, described by Martínez (2019), which consists on the systematic application of a Complete Scanning (CS) described by Bossa (2023) + Basic Protocol (Figure A) + Gynecological SYS (Figure B) + Endocrinological SYS (Figure C) + Biomagnetic Pairs (BMPs) = Fallopian Tube/Fallopian Tube and Uterus/Uterus (Figure D). After performing the MB CS, a thorough scan of each BMP that forms the Gynecological SYS, the Endocrinological SYS plus the Fallopian Tube/Fallopian Tube and Uterus/Uterus PBMs is carried out. The PTUM can be repeated as many times as necessary.
Figure A: Basic Protocol Biomagnetic Pairs (BMPs)

Caption: Illustrative photographic image of the application of the MB magnets on the anatomical points, north pole (red color) and south pole (black color) of the BMPs. Numbers 1 to 12 identify the BMPs that form the Basic Protocol. R (right); L (left); CL (contralateral); ¾ (between the third and fourth lumbar vertebra).
Source: Bossa (2021).
Figure B: Biomagnetic Pairs of the Gynecological System (Gynecological SYS)

Caption: Illustrative photographic image of the application of the MB magnets on the anatomical points, north pole (red color) and south pole (black color) of the BMPs respectively. Numbers from 1 to 10 identify the BMPs that form the Gynecological SYS. R (right); L (left); CL (contralateral); IPS (ipsilateral).
Source: Bossa (2021).
Figure C: Biomagnetic Pairs of the Endocrinological System (Endocrinological SYS)

Caption: Illustrative photographic image of the application of the MB magnets on the anatomical points, north pole (red color) and south pole (black color) of the BMPs. Numbers 1 to 9 identify the BMPs that form the Endocrinological SYS. R (right); L (left); CL (contralateral); Ant. (Anterior or ventral); Post. (posterior or dorsal).
Source: Bossa (2021).
Figure D: Biomagnetic Pairs Right Fallopian Tube/Left Fallopian Tube and Right Uterus/Left Uterus
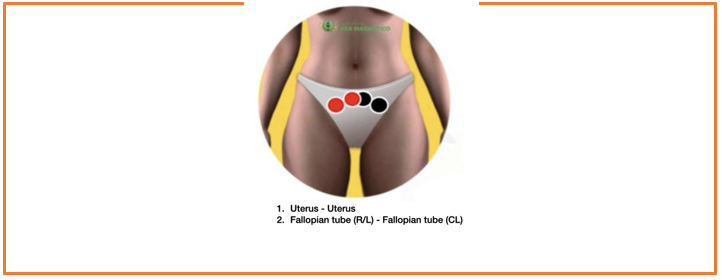
Caption: Illustrative photographic image of the application of the MB magnets on the anatomical points, north pole (red color) and south pole (black color) of the BMPs. Source: Bossa (2021).
4. DISCUSSION
According to Biomagnetic and Bioenergetic concepts, Dr. Goiz establishes that uterine fibroids are contained within a process of tumor genesis. The evolution of the tumor process is conditioned to triggering factors and occur progressively with the presence of DNA viruses that damage the cell membrane; the presence of other elements that alter the cell’s cytoplasm and its pH; other natural elements of inflammation in cellular nature; structural RNA viruses that unbalance the behavior of the cell nucleus and, therefore, of the genetic codes; the presence of an element that will give the location to the phenomenon; and finally, another that will give it the form and characteristic of malignancy, which is the leprosin protein produced by Mycobacterium leprae (DURÁN, 2003).
As reported by Dr. Goiz, myomas can be classified as true uterine myoma or false myoma. The one considered as true uterine myoma is manifested by the microorganisms Mycobacterium leprae, Papilloma virus, Bordetela pertussis and Chlamydia trachomatis. The false myoma is manifested by the microorganisms Enterobacter cloacae, Parvovirus and Varicella virus (DURÁN, 2003).
For MB, true uterine myoma is related to the following BMPs: Scapula (R/L) /Scapula (CL), Vagina (R/L) /Vagina (CL), Larynx (SUP/INF) and Duodenum/Kidney (L). The false myoma is manifested by the Biomagnetic Pairs: Descending Colon/Descending Colon (INF), Fallopian Tube (R/L)/Fallopian Tube (CL) and Ureter/Ureter. These BMPs may be associated with pathogenic microorganisms as a primary factor in the tumor. Food, smoking and drugs are associated as a secondary factor (DURÁN, 2003).
The Complete Screening (CS), performed as described by Bossa (2023) and CORRÊA et al. (2023), is considered the gold standard protocol of the MB. It serves as a prevention and treatment for any disease, including uterine fibroids that are supported by BMPs (DURÁN, 2008 and 2014; MARTÍNEZ, 2018; CORRÊA et al., 2023). The CS must be applied whenever treatment begins, and its action can be enhanced with the application of specific protocols for different pathologies, such as the Basic protocol, Gynecological System, Endocrinological System that constitute the PTUM (MARTÍNEZ, 2019; BOSSA 2023; CORRÊA et al., 2023).
Goiz (2003), in his work, The Tumor Phenomenon, describes the MB as an integrative and complementary tool for the treatment of tumors and cancers. Because it is a focused, evolutionary pathology, with relatively slow growth, it allows its bioenergetic and biomagnetic study, through the diagnosis and treatment of BMPs with the static magnetic fields generated by the therapeutic magnets of MB. In the long term, the MB allows the prevention of these complex pathologies, treating in advance the bioelectromagnetic dysfunctions of the factors that intervene in the genesis, stability, location, growth and final behavior of the tumors phenomena.
A study was carried out to investigate the invasion of human cervical carcinoma cell lines to positive human papillomavirus (HPV) into extracellular matrices leiomyoma-based to test the suitability of the model to study the effects of irradiation on cancer cells. In this study, the HPV virus (Papiloma virus) was found in uterine myoma tumor cells (TUOMINEN, 2020). Dr. Goiz also cites that the papilloma is present in a Biomagnetic Pair for the treatment of uterine myoma (DURÁN, 2003).
In another study of Bacteria associated with bacterial vaginosis and uterine fibroids (MOORE et al., 2021), Chlamydia Bacteria related to myoma was identified in PCR samples. Dr. Goiz (2003), declares that this bacteria is present in a BMP related to uterine fibroids. This study also relates uterine myoma to secondary factors alcohol, smoking and a greater number of sexual partners.
Martini et al. (2023) presented a case study in which the MB technique was applied in the treatment of prostatic adenocarcinoma, relating the treatment of BMPs with static magnetic fields generated by therapeutic magnets. After three sessions of MB, the levels of prostate specific antigen (PSA) decreased and the prostate adenocarcinoma regressed to discrete chronic inflammation, without the use of any other therapeutic intervention, showing that BMPs may be related to the support of pathologies as suggested by Goiz (2003).
According to the above and the concepts of MB for the treatment of pathologies such as uterine fibroids, the location of BMPs that allow the development and evolution of tumors is of fundamental importance. Pathogenic control, through strengthening the immune system can occur preventively or during treatment. This is done through CS. Thus, we have the Basic Protocol and Scanning by Endocrinological and Gynecological System (SYS) as complementary to the Complete Scanning, contemplating the Protocol for the Treatment of Uterine Myoma (PTUM), described by Martínez (2019) and Bossa (2021), in the treatment and prevention of uterine fibroids.
The Basic Protocol works on three main aspects of health by integrating detoxification, immune modulation and the treatment of chronic stress. The SYS were created from the CS in order to ensure that all BMPs to be treated are impacted by specific pathology, as well as to ensure that no BMP goes unnoticed by the CS. Scanning by Systems (SYS) enables a complementary treatment to investigate chronic diseases, where many organic systems are already involved in producing symptoms (MARTÍNEZ, 2018, BOSSA 2023).
Application of specific MB protocols can potentiate the effects of the CS, helping to strengthen the bioenergetic systems of organs and tissues, in addition to personalizing patient care, due to the thorough scanning, known as Fine Scanning (BOSSA, 2021) performed with the magnets on the BMPs of each SYS. Fine Scanning is also indicated in cases of energy blockage, magnet-resistance and BMPs that are repeated in the CS (MARTÍNEZ, 2018). It is performed with the help of a therapist assistant who moves the North Pole magnet, known as a tracker, on a specific anatomical area, and the Biomagnetism therapist monitors the body’s response to find the best anatomical point for the treatment of BMP. This allows better detoxification of the body, strengthens the immune system and improves metabolism, justifying the use of protocols for diseases such as PTUM (MARTÍNEZ, 2019, BOSSA 2021).
5. CONCLUSION AND PERSPECTIVES
Medicinal Biomagnetism is a non-invasive, easy-to-apply therapeutic system that seeks to correct bioenergetic dysfunctions and tissue pH, and can collaborate in a complementary way in the treatment of uterine fibroids, through the Protocol for the Treatment of Uterine Myomas. The PTUM can be used by health professionals, therapists or people who focus on disease prevention and treatment without neglecting the preventive principle, proposed by the PICS, to simply encourage self-care and self-management of quality of life.
This study is unprecedented and the first that points to the use of a MB protocol as an aid in the treatment of uterine fibroids (myoma) and may stimulate further studies in this field. Expectations are that PTUM will be integrated into the therapeutic conduct of Biomagnetism therapists and that it will be the first step towards new discussions about alternative and complementary measures adopted for the prevention and treatment of this disease in the practice of MB and, finally, that it will stimulate clinical trials so that evidence can be presented.
REFERENCES
BARCELOS, Natane B.; SOUZA, Vinícius G.; ASSIS, Natália L.; PINTO, Sebastião A.; CARVALHO, Pedro Henrique A.; MIRANDA, Carla S.S.; CARVALHO, Aparecida de Lourdes. Jornal Brasileiro de Patologia e Medicina Laboratorial, 2021. Disponível em:https://SciELO – Brasil – Clinicopathological study of cystic and atypical uterine leiomyoma: a rare entity Clinicopathological study of cystic and atypical uterine leiomyoma: a rare entity https://doi.org/10.5935/1676-2444.20210027. Accessed in November 2022
BOSSA, Adriane Viapiana. Protocolo de Rastreio do Biomagnetismo Medicinal. 2a Ed. Independente, janeiro de 2023; Cascavel/PR. Available at www.institutoparmagnetico.com.br
BOSSA, Adriane Viapiana. Biomagnetismo Medicinal Avançado, Bioenergética e Desbloqueio Emocional Magnético Avançados. 2. ed. Cascavel: Instituto Par Magnético, 281 p., 2021.
BOSSA, Camila V.; VIAPIANA, Cristiane; PERSON, Ivan. G.; LIMA, Márcia M.O. e BOSSA, Adriane Viapiana (2023). Fundamentals of Medicinal Biomagnetism. Health and Society, 3(01), 312–344. https://doi.org/10.51249/hs.v3i01.1178.
BROERINGMEYER, Richard. Princípios de la terapia magnética, 1991.
CORRÊA, Letícia M. R.; RAMBO, Rui; RAMBO, Marilene. C.; MARTINI, Angela. M. R.; LIMA, Márcia O.e BOSSA, Adriane. V. (2023). Apresentação de um Protocolo de Exame Físico (Triagem Biomagnética ou Bioenergética) e Semiologia para a Aplicação da Técnica de Biomagnetismo Medicinal: revisão narrativa. Health and Society, 3(01), 345–367. https://doi.org/10.51249/hs.v3i01.1179.
DURÁN, Isaac Goiz. El Fenômeno Tumoral. 3 Ed. Texcoco: Impressiones Emmanuel, 2003.
DURÁN, Isaac Goiz. MENDOZA CASTELÁN, Guillermo; MENDOZA CASTELÁN, Pedro. Par Biomagnético, Biomagnetismo Médico Y Bioenergética, experiencias de curación, año 2005, tomo II. Chapingo, México D. F.: Universidad Autónoma Chapingo, 2005.
DURÁN, Isaac Goiz. El Par Biomagnético. 5. ed. Chapingo, México D. F.: Universidad Autónoma Chapingo, 171 p., 2008.
DURÁN, Isaac Goiz. Fisiopatología bioenergética. México City, México: Medicinas Alternativas y Rehabilitación S. A. de CV, 362p., 2014.
FRANK, Bryan L. Biomagnetic Pair Therapy and typhoid fever: a pilot study. Medical Acumputure. V.29, n 5, p. 308-312, 2017. Disponível em: (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29067141/)/. Accessed in November 2022.
FREITAS, Ricardo. Metodologia Científica: Um Guia Prático Para Profissionais da Saúde. 1. ed. Petrolina-PE, 2017.
MARTINI, Angela Mara Rambo, CAZELLA, Luciane Neris, MARTINI, Yuri, BOSSA, Adrianee Viapiana e SANTOS, Jefferson Souza (2023). BIOMAGNETISMO MEDICINAL NO TRATAMENTO DO CÂNCER DE PRÓSTATA: UM ESTUDO DE CASO. Health and Society, 3(01), 438–464. https://doi.org/10.51249/hs.v3i01.1182
MARTÍNEZ, David Goiz. Manual del biomagnetista. Ciudad de México: Biomagnetism Research Institute, 2018.
MARTÍNEZ, David Goiz. Protocolos de Biomagnetismo. Ciudad de México: Biomagnetism Research Institute, 2019.
ISER, Maria Luiza A. KRACIK.; Pablo M. B. PEREIRA.; Betine P. M. Medicina Integrativa: um parecer situacional a partir da percepção de médicos do Sul do Brasil. Saúde em debate. Out-Dez 2019. DOI 10.1590/0103-1104201912309. Disponívelem:https://www.acielo..org/?q=medicina+integrativa&lang=pt&filter%5Bin %5D%5B%5D=scl/. Accessed in October 2022.
MOORE KR, Tomar M, Umbach DM, Gygax SE, Hilbert DW, Baird DD. Bacterial. Vaginosis-Associated Bacteria and Uterine Fibroids: A Nested Case-Control Study. Sex Transm Dis. 2021 Nov 1;48(11):844-850. DOI: 10.1097/OLQ.0000000000001466. PMID: 33993160; PMCID: PMC8516695. https://www.pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29066031/. Accessed in November 2022.
PAVNA K. Brahma, KRISTINA M. Martel, Gregory M. CHRISTMAN, Future Directions in Myoma Research. Obstetrics and Gynecology Clinics of North America, Volume 33, Issue 1, 2006, Pages 199-224, ISSN 0889-8545, ISBN 9781416035367, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ogc.2005.12.011.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/artic le/pii/S0889854505000999).
TUOMINEN H, Al-SAMADI A, SALO T, RAUTAVA J. Modelos de matriz extracelular baseados em tecido de mioma humano para testar os efeitos da irradiação nas células positivas para HPV. Virol J. 2020 Jun 30;17(1):87. DOI: 10.1186/s12985- 020-01367-1. PMID: 32605632; PMCID: PMC7325078. https://www.pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32605632/. Accessed in November 2022.
1Studian Graduate Program in Biomagnetism and Bioenergy Applied to Health, Par Magnético Institute – IPM / Faculty of Governance, Engineering and Education of São Paulo – FGE. SP, Brazil.
2Co-supervising Professor Program in Biomagnetism and Bioenergy Applied to Health, Par Magnético Institute – IPM / Faculty of Governance, Engineering and Education of São Paulo – FGE. SP, Brazil.
3Advising Professor Program in Biomagnetism and Bioenergy Applied to Health, Par Magnético Institute – IPM / Faculty of Governance, Engineering and Education of São Paulo – FGE. SP, Brazil.
