LIPOASPIRAÇÃO MECÂNICA DE PAPADA: RELATO DE CASO
LIPOSUCCIÓN MECÁNICA DE PAPADA: REPORTE DE UN CASO
REGISTRO DOI: 10.69849/revistaft/th10249091334
Luciana Vieira de A. Soares1
Marivone Batista Ribeiro Polesso2
ABSTRACT
Beauty standards, especially those that emphasize symmetry and facial harmony, have influenced self-perception and self-esteem, resulting in an increase in the demand for aesthetic interventions. The presence of submental fat, or jowls, is a common aesthetic concern, and its reduction is crucial for facial harmonization. Different techniques, such as liposuction, are used to treat this condition, each with its advantages and limitations. This study aims to report a clinical case of mechanical liposuction of double chins, describing the procedure, the results obtained, and its implications for facial aesthetics. The case involves a 40-year-old patient who sought treatment to reduce submental fat and improve facial contour. After clinical evaluation, it was decided to perform mechanical liposuction. The procedure was performed at the specialization clinic in Orofacial Harmonization of the Faculty of Amazonas – IAES. Mechanical double chin liposuction has been shown to be effective in improving facial contour and reducing submental fat, with satisfactory aesthetic results. Procedure customization and close monitoring are essential for treatment safety and success.
Keywords: Jowls, Mechanical Liposuction, Facial Aesthetics, Deoxycholic Acid, Orofacial Harmonization.
RESUMO
Os padrões de beleza, especialmente aqueles que enfatizam a simetria e a harmonia facial, têm influenciado a autopercepção e a autoestima, resultando em um aumento na procura por intervenções estéticas. A presença de gordura submentoniana, ou papada, é uma preocupação estética comum, e sua redução é crucial para a harmonização facial. Diferentes técnicas, como a lipoaspiração, são usadas para tratar essa condição, cada uma com suas vantagens e limitações. Este trabalho tem como objetivo relatar um caso clínico de lipoaspiração mecânica de papada, descrevendo o procedimento, os resultados obtidos, e suas implicações na estética facial. O caso envolve uma paciente de 40 anos que procurou tratamento para reduzir a gordura submentoniana e melhorar o contorno facial. Após avaliação clínica, decidiu-se pela lipoaspiração mecânica. O procedimento foi realizado na clínica de especialização em Harmonização Orofacial da Faculdade do Amazonas – IAES. A lipoaspiração mecânica de papada demonstrou ser eficaz na melhoria do contorno facial e redução da gordura submentoniana, com resultados estéticos satisfatórios. A personalização do procedimento e o monitoramento rigoroso são essenciais para a segurança e sucesso do tratamento.
Palavras-chave: Papada, Lipoaspiração Mecânica, Estética Facial, Ácido Deoxicólico, Harmonização Orofacial.
1 INTRODUCTION
The beauty standards imposed by society have exerted a growing influence on the perception of personal image, highlighting symmetry and facial harmony as predominant aesthetic ideals. These references, widely disseminated through social media and popular culture, significantly affect self-esteem and self-perception, leading to an increase in the demand for aesthetic interventions. In this context, the presence of submental fat, commonly known as jowls, emerges as one of the most frequent concerns among individuals seeking to align with these patterns (1,2).
Facial aesthetics proves to be a crucial component not only in promoting well-being, but also in improving the quality of life of patients. Aesthetic procedures aimed at rejuvenating and perfecting the facial contour are increasingly valued for their positive impact on personal satisfaction and self-confidence. The reduction of double chins, notably, stands out for its significant contribution to the harmonization of the face, underlining the importance of effective therapeutic approaches in this field (3,4).
Consequently, the double chin, associated with aging, weight gain and genetic factors, is a relevant aesthetic concern, which directly affects the mandibular and cervical contour. Anatomical alterations, such as those mentioned, can generate dissatisfaction with one’s own image, which drives the search for appropriate aesthetic solutions. In the face of this growing demand, several treatment methods have been developed and improved to meet patient expectations (5,6).
In this sense, the available therapeutic options stand out, which include both non-invasive methods, such as cryolipolysis and radiofrequency, and surgical techniques, such as liposuction. Each approach has its advantages and limitations, depending on the patient’s profile and the desired results. Specifically, liposuction continues to be one of the most effective alternatives for the removal of localized fat, especially in the submental region (5,7).
Mechanical liposuction has gained prominence for its precision and effectiveness in removing fat. However, like any invasive procedure, it has both advantages and disadvantages. Among the main advantages, the efficient removal of significant volumes of fat in a single session and the durability of the results obtained stand out. On the other hand, the disadvantages include possible complications, such as bruises, infections, and irregularities on the surface of the skin (8,9).
In terms of safety, the complication rates associated with mechanical liposuction are relatively low, especially when the procedure is performed by qualified professionals in appropriate facilities. In Brazil, the popularity of this procedure reflects a global trend, where liposuction remains among the most frequently performed cosmetic surgeries. It is indicated mainly for patients with localized fat deposits that do not respond to conservative interventions, such as diet and exercise, while its contraindications encompass individuals with health conditions that increase surgical risk (10,11).
Additionally, patient satisfaction with the results of mechanical double chin liposuction tends to be high, especially when the procedure meets expectations of facial contour and definition. However, it is essential that patients are fully informed about the possibilities and limitations of the treatment, in order to ensure a satisfactory experience and results consistent with their expectations (5,8).
In addition to the aesthetic advantages, mechanical double chin liposuction can also provide significant psychological benefits. Studies indicate that improving facial appearance is closely linked to an increase in self-esteem and personal satisfaction. Patients who undergo this type of intervention often report greater confidence in their social interactions and improved overall well-being. These positive psychological effects reinforce the importance of aesthetic procedures that go beyond superficiality, addressing deeper issues related to self-perception and quality of life (8,12,13).
On the other hand, it is crucial to consider the potential complications associated with mechanical liposuction. Although complication rates are low, as mentioned earlier, the success of the procedure depends on a careful evaluation of the patient and strict adherence to safety protocols. Complications such as asymmetries, changes in sensitivity, and visible scarring can occur, especially in cases where the technique is not performed accurately. Therefore, the choice of qualified professionals and clear communication between specialist and patient about the expectations and risks involved are essential to minimize these adverse events and ensure satisfactory results (8,10,14).
Based on these considerations, the present study aims to report a clinical case of mechanical liposuction of double chins, detailing the process, the results obtained and its implications for facial contour and harmony.
2 CASE REPORT
Patient E.S.M.Z., 40 years old, female, attended the specialization clinic in Orofacial Harmonization of the Faculty of Amazonas – IAES, reporting as her main complaint: “I would like to improve the contour of my face and reduce the double chin, which has caused me aesthetic discomfort and affects my self-esteem.” The patient presented complaints related to the accumulation of submental fat, evidenced by a pronounced double chin that interferes with the harmony of the facial contour.
During the anamnesis, it was observed that the patient uses hormone replacement medication and is lactose intolerant. In addition, it has a history of high exposure to the sun, which may have contributed to the degradation of skin elasticity and fat accumulation in the submental region. The information was relevant for treatment planning, considering the potential implications of such conditions on recovery and aesthetic outcome.
Physical examination revealed a significant accumulation of fat in the submental region, with slightly flaccid skin. The mandibular contour was compromised by the double chin, which justified the need for intervention to restore facial harmony (Figures 1 A-C).
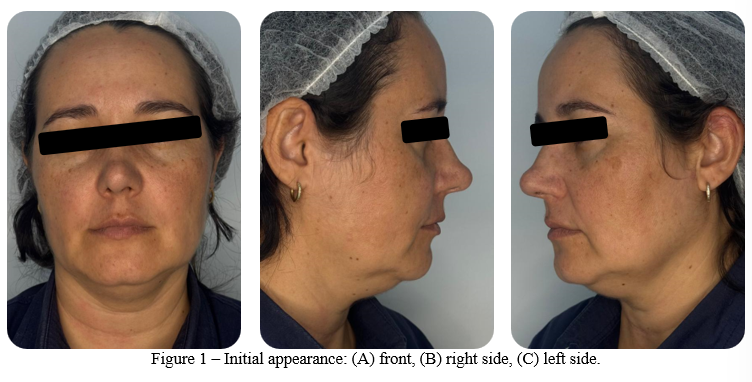
The proposed treatment was mechanical double chin liposuction. All associated risks, as well as the details of the proposed treatment, were clearly explained to the patient, including possible complications and the recovery process. After receiving and understanding all this information, the patient agreed to participate in the procedure and signed the Informed Consent Form and Image Use Authorization.
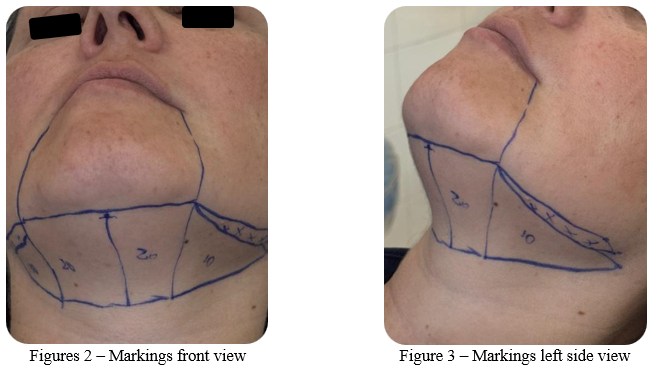
For the precise definition of the area to be treated, the patient was positioned in the dental chair at right angles, with the Frankfurt plane parallel to the ground. Using a surgical marking pen, the region of submental fat to be removed was delineated (Figures 2 and 3). The demarcation was performed with special attention to the area immediately above the hyoid bone and 10 mm below the base of the mandible, with the aim of protecting important anatomical structures, such as glands, vessels, and nerves. Thus ensuring a clear definition of the area to be aspirated, allowing precise and safe surgical planning for mechanical double chin liposuction.
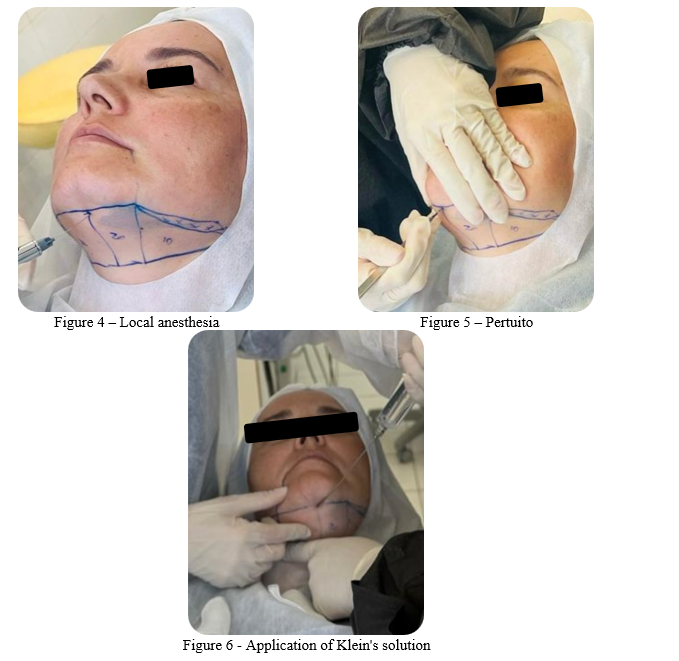
To perform mechanical liposuction of the double chin, an anesthetic button was applied 1 cm below the gnathium point (Figure 4). In this same location, a small incision of 0.5 mm was made in the dermis to allow the creation of the wig for insertion of the cannula (Figure 5). One hundred then, Klein’s solution was injected into the entire previously delimited region (Figure 6).
Klein’s solution was prepared according to the following formula: 04 drops of epinephrine, 04 ml of lidocaine, 04 ml of sodium bicarbonate and 32 ml of saline solution. This solution was carefully infiltrated into the submental area to promote vasoconstriction and analgesia, facilitating the removal of fat and minimizing discomfort during the procedure.
After 2 minutes, allowing the onset of the anesthetic effect, a single-hole cannula was introduced between the dermis and the platysmal fascia, connected to the vacuum suction pump hose. The procedure began with fan movements, alternating from right to left and left to right, with the aim of releasing the fibrous septal attachments between the subdermal layer and the platysmal fascia. This fan motion helps to detach the fat tissue from the underlying fascia, making it easier to remove fat.
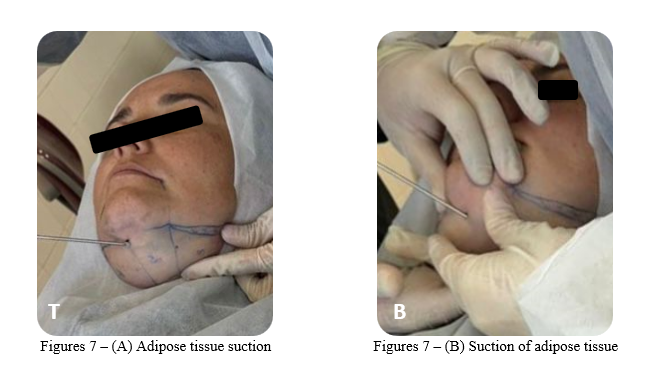
Then, the adipose tissue was aspirated through the vacuum pump for 30 minutes. The aspiration technique focused on removing the surrounding adipose tissue and promoting tissue tunneling, which aids in the contraction and formation of collagen, thereby improving the contour of the neck. Tunneling with the cannula was performed in linear and uniform lines, with the surgeon’s dominant hand controlling the cannula and the other hand adjusting the position of the instrument during the movements (Figures 7 A-B).
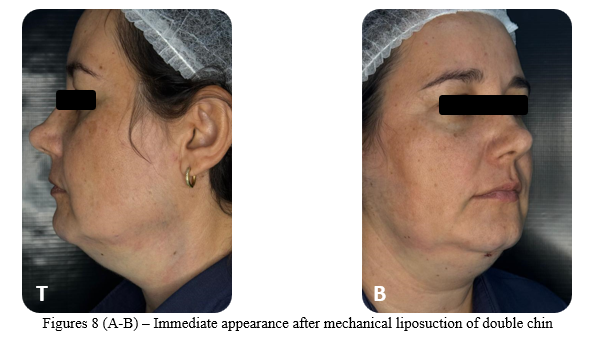
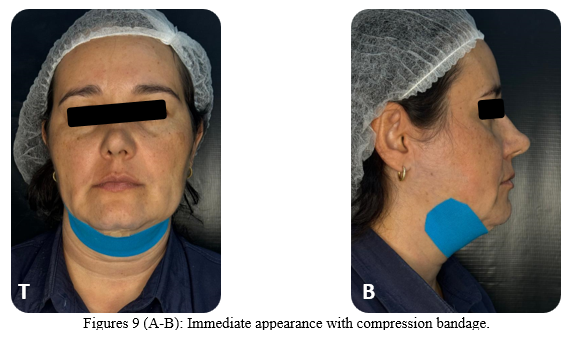
Finally, a “milking” was performed with both hands, from bottom to top and towards the incision, to drain all the fluid and floating blood, with the intention of preventing postoperative edema and hematomas. The access incision was sutured with 4-0 nylon thread (Figures 8 A-B). A compression band was applied over the site, and postoperative guidance was provided to the patient to ensure adequate recovery (Figures 9 A-B).
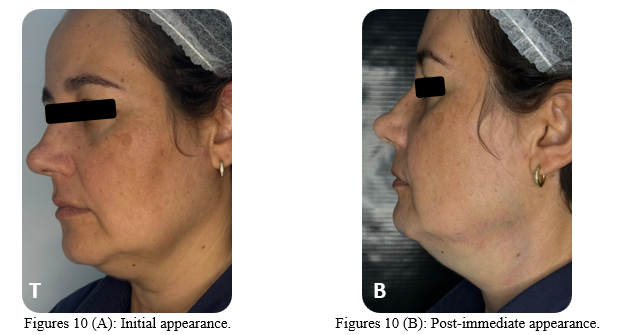
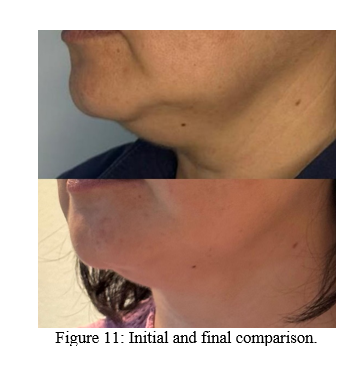
Immediately after liposuction, the results before and after the procedure were compared. A significant improvement in the contour of the face and a visible reduction of the double chin were observed, evidencing the effectiveness of the technique applied (Figures 10 A-B).
In the postoperative period, the patient was prescribed dipyrone 500 mg, to be administered every 4 hours in case of pain in the first 24 hours. In addition, the use of Diprospan 1 tablet intramuscularly has been recommended to aid in the reduction of inflammation and edema. The postoperative guidelines included care for the treated area and the importance of following medical recommendations to ensure adequate recovery and optimized results.
3 DISCUSSION
Mechanical double chin liposuction, as discussed in the clinical case described, is a technique that aims to improve facial contour, especially in patients with submental fat accumulation (8). According to Fernandes (5), double chin liposuction is effective in redefining the facial contour and improving the aesthetics of the neck, corroborating the choice of procedure for the patient in the case presented. Moneró et al. (7) emphasize that, when combined with non-invasive techniques, liposuction can provide significant aesthetic results, in line with the objective of the treatment proposed for our patient.
The study by Leite et al. (10), which discusses the limitations of liposuction, especially in terms of complications and the need for additional techniques to achieve optimal results. Shridharani and Chandawarkar (15) suggest that liposuction can lead to irregularities on the surface of the skin and that combination with additional techniques, such as the use of deoxycholic acid, may be necessary to improve outcomes. This aspect highlights the importance of careful planning and the choice of complementary techniques, such as the inclusion of deoxycholic acid in the patient’s treatment.
The use of Klein’s solution, as described, is widely accepted for infiltration during liposuction due to its vasoconstrictor and anesthetic properties (16). According to Morales López (17), Klein’s solution reduces bleeding and improves the precision of liposuction, which is in line with the approach adopted in the patient’s case. Del Vecchio et al. (18) highlight that adequate infiltration of Klein’s solution contributes to a better visualization of adipose tissue and facilitates its removal.
However, Del Vecchio et al. (18) suggest that the efficacy of Klein’s solution may vary depending on the individual characteristics of the patients and the technique used. They point out that, in some cases, the solution may not be sufficient to fully control bleeding, requiring the use of additional techniques to ensure optimal results. This point highlights the need to evaluate each patient individually and adjust the techniques as necessary, which was considered in the approach to the patient in the case presented.
The tunneling technique, performed in linear and uniform movements, is essential to ensure the efficient removal of adipose tissue and promote collagen formation, as described by Lima (19). Marten and Elyassnia (20) They state that performing controlled movements during liposuction is crucial to avoid the formation of irregularities and improve the contour of the neck. In the case of the patient, the careful application of this technique helped to achieve a satisfactory aesthetic result.
On the other hand, Bhojwani’s study (21) notes that improper tunneling can lead to complications such as irregular contours and unsatisfactory aesthetic results. They emphasize the importance of precise technical execution and strict postoperative follow-up to minimize risks. This aspect was carefully monitored in the patient’s case, with measures to prevent edema and bruising and ensure a consistent final result.
Performing “milking” to drain fluids and free-floating blood is an important practice to avoid postoperative complications. According to Zingaretti et al. (22), the post-liposuction drainage technique is effective in reducing the risk of hematomas and edema, which is confirmed by the protocol followed in the treatment of the patient. Zingaretti et al. (22) They highlight that adequate drainage contributes to a faster recovery and to obtaining more predictable results.
Postoperative follow-up and guidance provided to the patient are essential to ensure recovery and satisfaction with the results. According to Richards, Schleicher and Zins (23), adherence to postoperative guidelines and the use of appropriate medications are crucial to minimize discomfort and improve final aesthetics. In the case of the patient, the administration of dipyrone and Diprospan, as well as the use of a compression band, were essential measures to ensure a smooth recovery and a satisfactory aesthetic result.
This clinical case of mechanical double chin liposuction for the patient exemplifies the effectiveness of the technique when well planned and executed. The combination of liposuction, Klein solution infiltration, and complementary techniques such as the use of deoxycholic acid and adequate drainage demonstrate the importance of a multifaceted approach to achieve optimal results and minimize risks. The reviewed literature offers support for the techniques used and highlights the need for personalized adjustments according to the characteristics of each patient.
Although mechanical double chin liposuction was effective for the patient, some limitations are important. A significant limitation of this study is that it relies on a single case of mechanical double chin liposuction. The analysis was performed exclusively with one patient, which limits the generalizability of the results to a broader population. Studies with larger sample sizes are needed to validate the efficacy and safety of the technique in different patient profiles and to identify variations in results and possible complications. The inclusion of a diverse population would allow for a more comprehensive evaluation of the technique and contribute to the development of more robust guidelines that are adaptable to the varied needs of patients.
4 CONCLUSION
It is concluded that mechanical double chin liposuction can be effective to improve facial contour and reduce submental fat. The treatment presented satisfactory aesthetic results and was successfully performed. Procedure customization and close monitoring remain crucial to optimize outcomes and ensure patient safety.
REFERENCES
1. Marinho B, Gonçalves J, Perdigão N, Serafim G. Resultados do HIFU na redução do volume submandibular: uma análise detalhada. Rev Científica Ipedss. 2023;03(02):1–10.
2. Oliveira MC, Costa RP. Busca por perfeição estética x saúde: imposição social sobre a beleza. Brazilian J Heal Rev. 2021 Nov 17;4(6 SE-Original Papers):25398–406.
3. Albuquerque KLC de, Silva LB da, Teixeira HS. Autoestima e qualidade de vida: uma relação com a estética. Res Soc Dev. 2022;11(16):e496111638541.
4. Silva SF da. Lipo de papada enzimática com ácido deoxicólico. J Multidiscip Dent. 2023 Dec 4;11(2 SE-Revisão de Literatura):80–5.
5. Fernandes L. Lipoaspiração de papada para o rejuvenescimento facial: relato de caso. Aesthetic Orofac Sci. 2022 Jul 16;3(2):25–36.
6. Oliveira TAV da S, Moreira AG. Lipectomia cervicomentual. Simmetria Orofac Harmon Sci. 2022;4(13):62–70.
7. Veiga Moneró E, Yokota Guedes R, Luiza Siqueira Borges M, Borges Matos A, Paiva do Nascimento K, Raquel de Sousa Silva L, et al. Eficácia e segurança da criolipólise na redução de gordura submentoniana: uma revisão integrativa. Brazilian J Implantol Heal Sci. 2024 May 18;6(5 SE-Revisão de Literatura):1324–37.
8. Ferrão Júnior JP, Cordeiro LBST, Azevedo KMPF. Lipoaspiração submentual mecânica: um relato de caso clínico. Orofac Harmon. 2023;1(3).
9. Santos E, Lima M. Drenagem linfática no pós-operatório em lipoaspiração. Medicus. 2020;2(2):30–6.
10. Leite AMCS, Leite ICS, Rosa ML da S, de Almeida RM, Santos MVM, de Carvalho CCT, et al. Complicações em cirurgias e procedimentos lipoaspirativos: uma revisão da literatura. Arq Ciências da Saúde da UNIPAR. 2023 Jul 20;27(7):3624–31.
11. Barbosa MMS, Napoleão LD, Oliveira SV, Amâncio N de FG. Cirurgia plástica no Brasil: aspectos relacionados ao pré e pós-operatório. Peer Rev. 2024 Jan 19;6(1):362–77.
12. Salomão AC de M, Silva LL de O, Santos JR. Benefícios dos procedimentos estéticos na melhora da autoestima. Res Soc Dev. 2021;10(16):e590101624308.
13. Lira FKA, Silveira MR, dos Santos BLM, Linhares Filho AHF, Cavalcante MC da S, de Sá Costa AVB, et al. Avaliação dos efeitos neurobiológicos e psicológicos dos procedimentos estéticos. Brazilian J Dev. 2023 May 17;9(05 SE-Original Papers):16742–57.
14. Cárdenas-Camarena L. Lipoaspiration and its complications: a safe operation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003 Oct;112(5):1433–5.
15. Shridharani SM, Chandawarkar AA. Injection Adipocytolysis with ATX-101 (Deoxycholic Acid) for Body Contouring. Vol. 5, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Global Open. 2017.
16. Goyal NN. Tumescent anaesthesia for liposuction surgery: A review. Dermatological Rev. 2021;2(4):180–7.
17. Morales López L, Morales-Castellanos G. Valores hemáticos en pacientes sometidos a liposucción con anestesia general más solución de Klein sin lidocaína. Mediciencias UTA. 2019 Jun 1;3(2 SE-Artículo original de investigación):64–8.
18. Del Vecchio D, Wall Jr. S, Stein MJ, Jovic TH, Whitaker IS. Simultaneous Separation and Tumescence: A New Paradigm for Liposuction Donor Site Preparation. Aesthetic Surg J. 2022 Dec 1;42(12):1427–32.
19. Lima EV de A. Dermal tunneling: a proposed treatment for depressed scars. An Bras Dermatol. 2016 Oct;91(5):697–9.
20. Marten T, Elyassnia D. Neck Lift: Defining Anatomic Problems and Choosing Appropriate Treatment Strategies. Clin Plast Surg. 2018 Oct;45(4):455–84.
21. Bhojwani A. Addressing the “Double Chin:” Trends in Submental Contouring. J Dermatology Cosmetol. 2016;1(1).
22. Zingaretti N, Albanese R, Pisano G, Isola M, Giusti A, De Martino M, et al. Evaluation of Kinesio Taping for Edema, Ecchymosis, and Pain After Liposuction: A Prospective Pilot Study. Aesthetic Surg J. 2023 Sep;43(10):NP787–96.
23. Richards BG, Schleicher WF, Zins JE. Putting it all together: recommendations for improving pain management in plastic surgical procedures-surgical facial rejuvenation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014 Oct;134(4 Suppl 2):108S-112S.
1 Specialist in Orofacial Harmonization
Institution: Faculdade do Amazonas – IAES (Manaus, AM)
2 Specialist in Orofacial Harmonization
Institution: Faculdade do Amazonas – IAES (Manaus, AM)
