REGISTRO DOI: 10.69849/revistaft/pa10202505311812
Célio Francisco Filho1
Abstract
This article examines the industrial transformation led by Brazilian engineer Celio Francisco Filho through the implementation of a state-of-the-art production line for metalized solar protection glass in Brazil. Drawing on advanced sputtering technology acquired during a specialization course in Germany, Celio successfully adapted European precision engineering to the challenges of Brazil’s climate and infrastructure. The result is a fully automated manufacturing process capable of depositing nanometric metallic layers on architectural glass, offering superior solar control and energy efficiency for buildings in hot climate zones. The study highlights the project’s alignment with Industry 4.0 principles, featuring real-time monitoring systems, predictive maintenance, and digital integration for optimal operational performance. In addition to technological advances, the initiative emphasizes sustainable manufacturing practices, such as closed-loop water recycling and low-emission vacuum deposition, making it compatible with global green building certifications. The article also explores the project’s social impact, including the training of a new generation of professionals in high-tech manufacturing and the strengthening of research partnerships between industry and academia. Through this case study, the paper demonstrates how the transfer and contextualization of international expertise can catalyze innovation and set new benchmarks for industrial development in Latin America.
Keywords: Solar protection glass, sputtering deposition, Industry 4.0, sustainable manufacturing, Brazilian industrial innovation.
Behind the cutting-edge production line of metalized solar protection glass in Brazil is a strategic mind that has transformed technical knowledge into industrial innovation: Celio Francisco Filho, a mechatronic engineer with over a decade of experience in the glass manufacturing industry. Celio has played a pivotal role in bringing this transformative project to life, implementing a fully automated, state-of-the-art production line inspired by advanced German technology.
Celio’s journey began with a specialization course in Germany, where he immersed himself in the latest advancements in metallic deposition processes and solar control technologies applied to architectural glass. “It was an experience that changed my perspective entirely. German factories operate with millimetric precision and embrace sustainability as a default standard. My goal was to bring the best of that technology here, adapting it to our reality and tropical climate,” Celio explains.
The production line he helped implement is one of the first in Brazil to utilize sputtering technology in a controlled environment. This sophisticated process enables the deposition of ultra-thin metal layers—measured at the nanometer scale—onto large glass panels. The result is glass with highly effective solar control, capable of reducing thermal gain while preserving natural light transmission. The implications for energy efficiency in buildings are significant, especially in hot climate zones where air conditioning usage can be excessive.
Celio’s involvement spanned the entire project lifecycle, from selecting equipment and designing the plant layout to hiring and training personnel. He also led initial testing with various metallic substances, including silver, chromium, and metal oxides, to achieve optimal optical and thermal performance. “Installing machines is not enough. You must understand the behavior of glass at each stage and integrate engineering, automation, and quality control seamlessly,” he emphasizes.
Thanks to Celio’s technical leadership, the factory now produces high-performance glass that can reduce heat ingress by up to 70%. This contributes directly to lower energy consumption in both commercial and residential buildings. In doing so, the factory has positioned itself as a benchmark for sustainability and technological innovation within the construction industry. According to recent studies, low-emissivity (low-E) coatings and solar control glazing can dramatically improve building energy efficiency (Cuce et al., 2016; Baetens, Jelle, & Gustavsen, 2010).
Celio credits his international training not only with deepening his technical expertise but also with broadening his understanding of logistical, regulatory, and environmental challenges associated with the production of smart glass. “There, I realized how vital investment in research and development is. We brought that mindset back to Brazil, forging partnerships with universities and technology centers. This project goes far beyond glass—it’s about transforming our national industry,” he says.
The glass produced in this advanced facility is coated with noble metals or oxides under vacuum conditions, forming layers that act as a solar filter. These layers reflect infrared radiation and block up to 99% of ultraviolet rays. Such properties make metalized glass highly desirable for building facades, skylights, and energy-efficient residential applications (Selkowitz, 1999; U.S. Department of Energy, 2021).
Celio’s work exemplifies how international expertise, when thoughtfully adapted and applied to local contexts, can drive significant industrial progress. By merging German technological precision with Brazilian innovation and climate considerations, Celio Francisco Filho has set a new benchmark for the glass industry in Latin America—one that promises both environmental and economic benefits.
Another noteworthy aspect of the project is its integration with Industry 4.0 principles. The production line features real-time monitoring systems, predictive maintenance algorithms, and a centralized control interface that allows operators to adjust parameters with high precision. These innovations not only reduce downtime and operational costs but also enhance product uniformity and process traceability. Studies have shown that the application of Industry 4.0 in manufacturing environments significantly improves productivity and quality control, especially in sectors requiring high precision and customization, such as glass processing (Lasi et al., 2014; Zheng et al., 2021). “We’re not just producing advanced glass—we’re creating a digital ecosystem that ensures our processes are always optimized and sustainable,” Celio notes.
In addition to technological sophistication, the factory’s commitment to environmental responsibility is a defining feature of the initiative. It employs closed-loop water recycling, low-emission vacuum deposition systems, and energy-efficient infrastructure to minimize its environmental footprint. These practices are aligned with sustainable manufacturing frameworks that emphasize resource efficiency and lifecycle thinking (Jayal et al., 2010). The facility also complies with international standards related to eco-friendly construction materials, making it compatible with global green building certifications such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and BREEAM. Research has confirmed that energy-efficient glazing contributes significantly to reducing the embodied and operational energy of buildings (Pomponi & Moncaster, 2016).
The flowchart illustrates the key stages of an industrial innovation process led by Brazilian engineer Celio Francisco Filho, who introduced advanced German technology into Brazil’s glass manufacturing sector. It begins with international technical training and the transfer of sputtering technology, followed by the implementation of a fully automated production line, including equipment selection, layout design, and workforce training. The next stage involves a controlled sputtering process that applies nanometric metal layers to glass, resulting in products that offer high solar control and energy efficiency. The flow then highlights integration with Industry 4.0 systems—such as real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance—before moving on to sustainability practices and compliance with green building certifications. It concludes with the social and educational impact of the project, including local workforce development and collaboration with academic institutions.
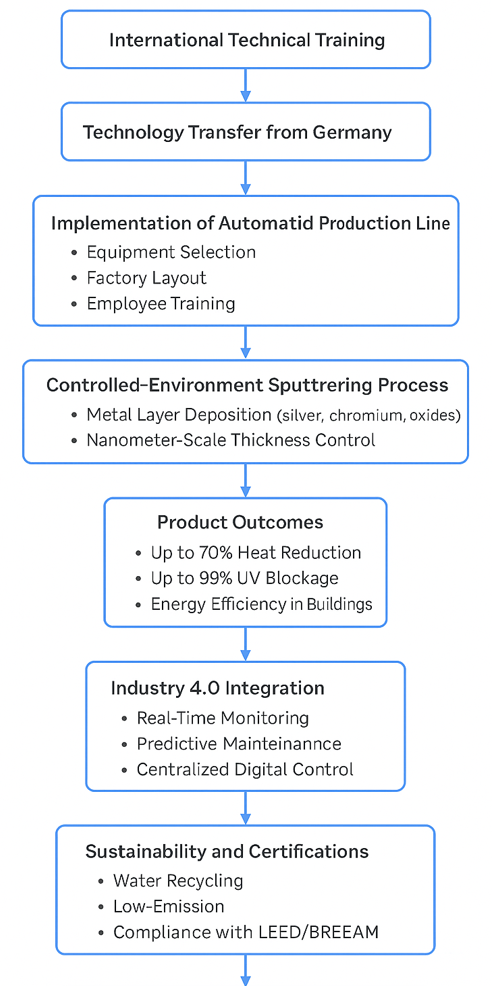
Figure 1. integration with Industry 4.0 systems.
Source: Created by author.
The social and educational dimensions of the project are equally transformative. By investing in workforce training and technical education, the initiative has contributed to the development of a new generation of skilled professionals in high-tech glass manufacturing. This is especially relevant in Brazil, where bridging the gap between industrial innovation and human capital remains a key development challenge. According to Schwab (2017), successful adaptation to the Fourth Industrial Revolution requires not only access to technology but also strategic investment in education and reskilling. Celio’s efforts reflect this ethos: “We’re not only building machines—we’re building people who can lead the industry into the future.”
References
Baetens, R., Jelle, B. P., & Gustavsen, A. (2010). Properties, requirements and possibilities of smart windows for dynamic daylight and solar energy control in buildings: A state-of-the-art review. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 94(2), 87–105.
Cuce, E., Cuce, P. M., & Riffat, S. B. (2016). A comprehensive review of solar control coatings for building integrated glazing applications. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 60, 1332–1353.
Jayal, A. D., Badurdeen, F., Dillon, O. W., & Jawahir, I. S. (2010). Sustainable manufacturing: Modeling and optimization challenges at the product, process and system levels. CIRP Journal of Manufacturing Science and Technology, 2(3), 144–152.
Lasi, H., Fettke, P., Kemper, H. G., Feld, T., & Hoffmann, M. (2014). Industry 4.0. Business & Information Systems Engineering, 6(4), 239–242.
Pomponi, F., & Moncaster, A. (2016). Embodied carbon mitigation and reduction in the built environment – What does the evidence say?. Journal of Environmental Management, 181, 687–700.
Schwab, K. (2017). The Fourth Industrial Revolution. World Economic Forum.
Selkowitz, S. (1999). High-Performance Glazing Systems: Architectural Opportunities for the 21st Century. Journal of the Illuminating Engineering Society, 28(1), 89–102.
U.S. Department of Energy. (2021). Energy Saver: Windows, Doors, and Skylights.
Zheng, P., Wang, H., Sang, Z., Zhong, R. Y., Liu, Y., Liu, C., … & Xu, X. (2021). Smart manufacturing systems for Industry 4.0: Conceptual framework, scenarios, and future perspectives. Frontiers of Mechanical Engineering, 16, 1–14.
Silva, J. F. (2024). SENSORY-FOCUSED FOOTWEAR DESIGN: MERGING ART AND WELL-BEING FOR INDIVIDUALS WITH AUTISM. International Seven Journal of Multidisciplinary, 1(1). https://doi.org/10.56238/isevmjv1n1-016
Silva, J. F. (2024). SENSORY-FOCUSED FOOTWEAR DESIGN: MERGING ART AND WELL-BEING FOR INDIVIDUALS WITH AUTISM. International Seven Journal of Multidisciplinary, 1(1). https://doi.org/10.56238/isevmjv1n1-016
Silva, J. F. (2024). Enhancing cybersecurity: A comprehensive approach to addressing the growing threat of cybercrime. Revista Sistemática, 14(5), 1199–1203. https://doi.org/10.56238/rcsv14n5-009
Venturini, R. E. (2025). Technological innovations in agriculture: the application of Blockchain and Artificial Intelligence for grain traceability and protection. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(3), e78100. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n3-007
Turatti, R. C. (2025). Application of artificial intelligence in forecasting consumer behavior and trends in E-commerce. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(3), e78442. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n3-039
Garcia, A. G. (2025). The impact of sustainable practices on employee well-being and organizational success. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(3), e78599. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n3-054
Filho, W. L. R. (2025). The Role of Zero Trust Architecture in Modern Cybersecurity: Integration with IAM and Emerging Technologies. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(1), e76836. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n1-060
Antonio, S. L. (2025). Technological innovations and geomechanical challenges in Midland Basin Drilling. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(3), e78097. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n3-005
Moreira, C. A. (2025). Digital monitoring of heavy equipment: advancing cost optimization and operational efficiency. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(2), e77294. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n2-011
Delci, C. A. M. (2025). THE EFFECTIVENESS OF LAST PLANNER SYSTEM (LPS) IN INFRASTRUCTURE PROJECT MANAGEMENT. Revista Sistemática, 15(2), 133–139. https://doi.org/10.56238/rcsv15n2-009
SANTOS,Hugo;PESSOA,EliomarGotardi.Impactsofdigitalizationontheefficiencyandqualityofpublicservices:Acomprehensiveanalysis.LUMENETVIRTUS,[S.l.],v.15,n.40,p.44094414,2024.DOI:10.56238/levv15n40024.Disponívelem:https://periodicos.newsciencepubl.com/LEV/article/view/452.Acessoem:25jan.2025.
Freitas,G.B.,Rabelo,E.M.,&Pessoa,E.G.(2023).Projetomodularcomreaproveitamentodecontainermaritimo.BrazilianJournalofDevelopment,9(10),28303–28339.https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv9n10057
Freitas,G.B.,Rabelo,E.M.,&Pessoa,E.G.(2023).Projetomodularcomreaproveitamentodecontainermaritimo.BrazilianJournalofDevelopment,9(10),28303–28339.https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv9n10057
Pessoa,E.G.,Feitosa,L.M.,ePadua,V.P.,&Pereira,A.G.(2023).EstudodosrecalquesprimáriosemumaterroexecutadosobreaargilamoledoSarapuí.BrazilianJournalofDevelopment,9(10),28352–28375.https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv9n10059
PESSOA,E.G.;FEITOSA,L.M.;PEREIRA,A.G.;EPADUA,V.P.Efeitosdeespéciesdealnaeficiênciadecoagulação,Alresidualepropriedadedosflocosnotratamentodeáguassuperficiais.BrazilianJournalofHealthReview,[S.l.],v.6,n.5,p.2481424826,2023.DOI:10.34119/bjhrv6n5523.Disponívelem:https://ojs.brazilianjournals.com.br/ojs/index.php/BJHR/article/view/63890.Acessoem:25jan.2025.
SANTOS,Hugo;PESSOA,EliomarGotardi.Impactsofdigitalizationontheefficiencyandqualityofpublicservices:Acomprehensiveanalysis.LUMENETVIRTUS,[S.l.],v.15,n.40,p.44094414,2024.DOI:10.56238/levv15n40024.Disponívelem:https://periodicos.newsciencepubl.com/LEV/article/view/452.Acessoem:25jan.2025.
Filho, W. L. R. (2025). The Role of Zero Trust Architecture in Modern Cybersecurity: Integration with IAM and Emerging Technologies. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(1), e76836. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n1-060
Oliveira, C. E. C. de. (2025). Gentrification, urban revitalization, and social equity: challenges and solutions. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(2), e77293. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n2-010
Pessoa, E. G. (2024). Pavimentos permeáveis uma solução sustentável. Revista Sistemática, 14(3), 594–599. https://doi.org/10.56238/rcsv14n3-012
Filho, W. L. R. (2025). THE ROLE OF AI IN ENHANCING IDENTITY AND ACCESS MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS. International Seven Journal of Multidisciplinary, 1(2). https://doi.org/10.56238/isevmjv1n2-011
Antonio, S. L. (2025). Technological innovations and geomechanical challenges in Midland Basin Drilling. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(3), e78097. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n3-005
Pessoa, E. G. (2024). Pavimentos permeáveis uma solução sustentável. Revista Sistemática, 14(3), 594–599. https://doi.org/10.56238/rcsv14n3-012
Pessoa, E. G. (2024). Pavimentos permeáveis uma solução sustentável. Revista Sistemática, 14(3), 594–599. https://doi.org/10.56238/rcsv14n3-012
Eliomar Gotardi Pessoa, & Coautora: Glaucia Brandão Freitas. (2022). ANÁLISE DE CUSTO DE PAVIMENTOS PERMEÁVEIS EM BLOCO DE CONCRETO UTILIZANDO BIM (BUILDING INFORMATION MODELING). Revistaft, 26(111), 86. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10022486
Eliomar Gotardi Pessoa, Gabriel Seixas Pinto Azevedo Benittez, Nathalia Pizzol de Oliveira, & Vitor Borges Ferreira Leite. (2022). ANÁLISE COMPARATIVA ENTRE RESULTADOS EXPERIMENTAIS E TEÓRICOS DE UMA ESTACA COM CARGA HORIZONTAL APLICADA NO TOPO. Revistaft, 27(119), 67. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7626667
Eliomar Gotardi Pessoa, & Coautora: Glaucia Brandão Freitas. (2022). ANÁLISE COMPARATIVA ENTRE RESULTADOS TEÓRICOS DA DEFLEXÃO DE UMA LAJE PLANA COM CARGA DISTRIBUÍDA PELO MÉTODO DE EQUAÇÃO DE DIFERENCIAL DE LAGRANGE POR SÉRIE DE FOURIER DUPLA E MODELAGEM NUMÉRICA PELO SOFTWARE SAP2000. Revistaft, 26(111), 43. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10019943
Pessoa, E. G. (2025). Optimizing helical pile foundations: a comprehensive study on displaced soil volume and group behavior. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(4), e79278. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n4-047
Pessoa, E. G. (2025). Utilizing recycled construction and demolition waste in permeable pavements for sustainable urban infrastructure. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(4), e79277. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n4-046
Testoni, F. O. (2025). Niche accounting firms and the brazilian immigrant community in the U.S.: a study of cultural specialization and inclusive growth. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(5), e79627. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n5-034
Silva, J. F. (2025). Desafios e barreiras jurídicas para o acesso à inclusão de crianças autistas em ambientes educacionais e comerciais. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(5), e79489. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n5-011
POURRE, Carlla Brito Furlan. (2020). Indicadores de Resultados Finalísticos como Instrumento de Diagnóstico do Transporte Urbano: Um Estudo de Caso do Distrito Federal. Dissertação de Mestrado em Arquitetura e Urbanismo, Programa de Pós-Graduação em Arquitetura e Urbanismo, Faculdade de Arquitetura e Urbanismo, Universidade de Brasília, Brasília, DF, 167p. Disponível em: https://repositorio.unb.br/handle/10482/38743.
FURLAN, Carlla Brito; SANTOS, Gleys Ially Ramos dos. 2016. A qualidade do transporte público urbano em cidades médias: estudo de caso em Palmas-Tocantins. Revista em Gestão, Inovação e Sustentabilidade. Disponível em: chrome-extension://efaidnbmnnnibpcajpcglclefindmkaj/https://editora.iabs.org.br/site/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/ReGis-Dez-16-1.pdf.
POURRE, Carlla Brito Furlan. MAGALHÃES, Marcos Thadeu Queiroz; ROCHA Marecilda; Mello, Cristina de. 2022. Desempenho Urbano em uma Cidade Planejada (Palmas-To): Uma Leitura pela Sintaxe Espacial. Conference: Anais do Encontro Nacional da Associação Nacional de Pós Graduação e Pesquisa em Planejamento Urbano e Regional – XIX ENCONTRO NACIONAL DA ANPUR. Blumenau- SC. Disponível em: http://repositorio2.unb.br/jspui/handle/10482/47875.
MOYSÉS, David de Almeida; FERNANDES, Jorge Henrique Cabral; HOSOUME, Juliana Mayuni; PIÑA, Ana Beatriz Souza; BERNARDES, Marciele Berger; BAUCHSPIESS, Adolfo; POURRE, Carlla Brito Furlan; CARVALHO, Michele Tereza Marques; GARCIA, Luís Paulo Faina; BORGES, Geovany Araújo. 2022. Iniciativas experimentais. CESUs: Centros de Eficiência em Sustentabilidade Urbana (Livro) – Volume II: Aplicações. Editora Ecos. Disponível em: https://repositorio.ecos.unb.br/exhibits/show/editoraecos/item/554#?c=&m=&s=&cv=.
POURRE, Carlla Brito Furlan, MOYSÉS, David de Almeida, MAGALHÃES, Marcos Thadeu Queiroz, FERNANDES, Jorge Henrique Cabral Fernandes. 2022. Processos finalísticos de um CESU. CESUs: Centros de Eficiência em Sustentabilidade Urbana (Livro) Volume III: Proposições e Perspectivas. Editora Ecos. Disponível em: https://repositorio.ecos.unb.br/exhibits/show/editoraecos/item/563#?c=&m=&s=&cv=.
MAGALHÃES, Marcos Thadeu Queiroz; POURRE, Carlla Brito Furlan. 2022. Planejamento e smart cities. In: CESUs: Centros de Eficiência em Sustentabilidade Urbana (Livro) – Volume I: Fundamentos. Editora Ecos. Disponível em: https://repositorio.ecos.unb.br/exhibits/show/editoraecos/item/562#?c=&m=&s=&cv=.
Poure, C. B. F. (2024). UMA ANÁLISE BIBLIOMÉTRICA DA PESQUISA DE FRAMEWORK DE CIDADES INTELIGENTES. Revista Sistemática, 14(8), 591–605. https://doi.org/10.56238/rcsv14n8-009
Brito Furlan, C. ., & Ially Ramos dos Santos, G. . (2019). A Qualidade do Transporte Público Urbano em Cidades Médias: Estudo de Caso em Palmas – Tocantins. arq.Urb, (17), 75–88. Recuperado de https://revistaarqurb.com.br/arqurb/article/view/177
MELLO, Cristina Maria Correia de et al.. LOCALIZAÇÃO, ENCONTROS E ESQUIVANÇAS NOS CONJUNTOS HABITACIONAIS DO PMCMV: UM OLHAR SOBRE UMA EXPERIÊNCIA NO DISTRITO FEDERAL.. In: Anais do 5º Fórum HABITAR 2019: Habitação e Desenvolvimento Sustentável. Anais…Belo Horizonte(MG) UFMG, 2019. Disponível em: https//www.even3.com.br/anais/forumhabitar2019/197679-LOCALIZACAO-ENCONTROS-E-ESQUIVANCAS-NOS-CONJUNTOS-HABITACIONAIS-DO-PMCMV–UM-OLHAR-SOBRE-UMA-EXPERIENCIA-NO-DIST. Acesso em: 26/05/2025
Silva, J. F. (2024). SENSORY-FOCUSED FOOTWEAR DESIGN: MERGING ART AND WELL-BEING FOR INDIVIDUALS WITH AUTISM. International Seven Journal of Multidisciplinary, 1(1). https://doi.org/10.56238/isevmjv1n1-016
1Graduado em Engenharia Mecatrônica Universidade Cruzeiro do Sul – UNICSUL Endereço: (São Paulo , SP e Brasil) E-mail: celiofilho.77@gmail.com
