REGISTRO DOI: 10.69849/revistaft/ch10202504040724
Daniela de Mesquita Feijão
Abstract
The global population is aging rapidly, leading to a notable rise in chronic diseases among the elderly. This demographic shift presents significant challenges for healthcare systems, especially in terms of managing long-term care. Common chronic conditions among older adults include hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease. These conditions often require ongoing monitoring and management, posing both medical and logistical challenges for caregivers and healthcare providers. The epidemiology of chronic diseases in the elderly indicates an increasing prevalence, driven by aging, frailty, and the accumulation of multiple health conditions over time. As the elderly population grows, healthcare systems must adapt to address the complex needs of this group. Effective long-term care management is critical to maintaining a high quality of life, as older adults often experience not only physical health issues but also challenges related to dependence and a need for continuous support. Inadequate management of these chronic conditions can lead to poor health outcomes, including hospitalizations, diminished independence, and premature mortality. This article explores the key chronic diseases prevalent among the elderly, highlighting the increasing burden of multimorbidity. It also examines the unique challenges of managing long-term care for elderly patients, such as ensuring access to appropriate healthcare services, caregiver support, and patient adherence to treatment regimens. Furthermore, the article discusses strategies that have been implemented to improve the quality of care, including integrated care models, technological innovations, and the importance of patient-centered approaches. These strategies are vital in ensuring optimal outcomes for elderly individuals living with chronic conditions.
Keywords: Chronic diseases, Elderly, Long-term care, Epidemiology.
Global population is living longer, which directly leads to an increase in the number of elderly individuals with chronic diseases. These conditions, such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, Alzheimer’s, and osteoarthritis, not only affect the physical health of the elderly but also their cognitive, emotional, and social abilities. The presence of multiple chronic conditions in the same person, a phenomenon known as multimorbidity, has become a growing reality among the elderly, which poses additional challenges for healthcare professionals. The management of these conditions requires a holistic approach, which goes beyond medical treatment and includes the social and psychological aspects of the patients.
Aging brings increased frailty, which exacerbates chronic health conditions and makes treatment more complex. As a result, many elderly individuals live with these diseases for years, requiring continuous and personalized care. For these care efforts to be effective, it is crucial for healthcare professionals, such as doctors, nurses, physiotherapists, and nutritionists, to work together, offering a coordinated and integrated approach. Assistance to this population cannot be limited to treating the diseases themselves but must also encompass a broader view, considering the overall health status, emotional needs, and social factors affecting the elderly’s lives. Figure 1 shows the distribution of different chronic diseases among elderly individuals.
Long-term care management for the elderly also requires innovative solutions, such as the use of technology, which can enhance health monitoring and provide more efficient tracking, especially in remote areas or in settings with limited infrastructure. Technologies such as telemedicine and remote monitoring devices have shown to be effective in managing chronic diseases, providing greater convenience for patients and efficiency for healthcare professionals. However, it is necessary to ensure that these tools are accessible to all elderly individuals, regardless of socioeconomic level or familiarity with technology.
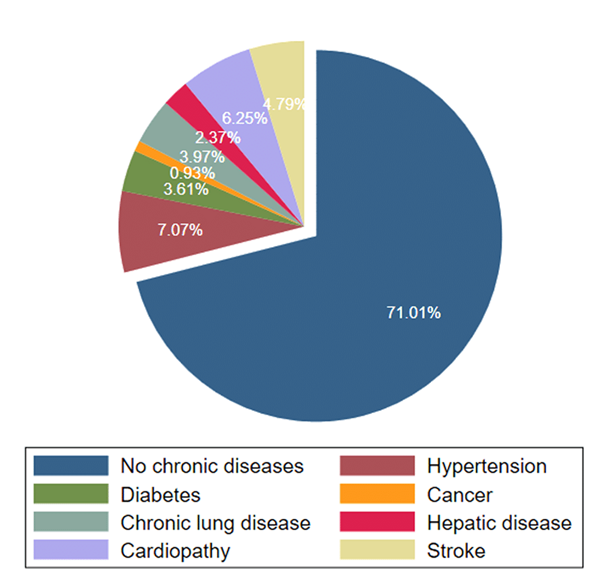
Figure 1: AI impact in mines according to employees.
Source: Xu et al., 2022.
Adherence to treatment is another critical issue in managing chronic diseases in the elderly. Often, elderly patients struggle to follow medical recommendations due to cognitive, physical, or social limitations. Therefore, public policies that promote health education and support programs for caregivers are essential to ensure that elderly individuals receive the necessary care and that their families receive the support needed to manage daily care. Trained caregivers play a crucial role, as they are often the primary individuals responsible for managing the elderly’s health conditions at home.
In the past five years, a series of studies have addressed the issues related to chronic diseases in the elderly and long-term care management. Oliveira et al. (2021) conducted a detailed analysis of the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases in the elderly and suggested that the development of integrated care, involving multiple healthcare professionals, is essential for managing multiple comorbidities. The authors also highlighted the importance of education programs for patients and caregivers, aiming to improve treatment adherence and, consequently, the quality of life of elderly individuals.
Santos and Ferreira (2020) investigated the implications of multimorbidity in geriatric care, analyzing how interactions between different chronic diseases complicate elderly health management. The results indicated that traditional treatment approaches are insufficient, requiring a personalized and coordinated plan that addresses both clinical and psychosocial aspects of patients.
Lima and Costa (2022) focused on the difficulties faced by developing countries in managing chronic diseases in the elderly. Their research revealed that the lack of adequate infrastructure and resources is one of the biggest barriers to implementing long-term care, especially in rural areas. Moreover, the study highlighted that training healthcare professionals and creating public policies are crucial to overcoming these challenges.
Sousa et al. (2021) analyzed the impact of technologies, such as telemedicine, in managing chronic diseases in the elderly. Their research concluded that these technologies have great potential to improve chronic disease control and reduce the need for frequent hospitalizations, although accessibility remains a challenge, especially in poorer communities.
Pereira and Almeida (2020) emphasized the importance of training family caregivers in managing chronic diseases, noting that many caregivers lack the necessary knowledge to cope with the demands of daily care. Training these caregivers not only improves the care provided to the elderly but also reduces the stress and emotional burden on family members.
Fernandes et al. (2022) conducted a review on the relationship between frailty and chronic diseases in the elderly, proposing a patient-centered care model that considers both the physical and cognitive/emotional conditions of elderly individuals. The authors stressed that frailty should be considered a determining factor in care planning, especially for vulnerable populations.
Rodrigues et al. (2023) investigated public policies for long-term care, highlighting the need to integrate primary and specialized care. The study suggested that implementing policies that favor the integration of these services could lead to better health outcomes for the elderly and simultaneously reduce healthcare system costs.
The rise in chronic diseases among the elderly represents a significant challenge for healthcare systems worldwide. Effective long-term care management for this population requires a comprehensive and multidisciplinary approach capable of addressing the complexity of health conditions and the multiple needs of this age group. Chronic disease treatment should be tailored to the physical, emotional, and social conditions of the patients, ensuring integrated and personalized care.
Moreover, it is essential for public policies to promote health education and caregiver support to ensure that elderly individuals adhere to medical recommendations and have access to necessary care. The use of technologies, such as telemedicine and remote monitoring devices, has proven to be a valuable tool in managing chronic diseases, providing more effective and accessible monitoring.
To face the challenges of aging and multimorbidity, it is crucial to coordinate healthcare services and promote patient-centered care. This will allow elderly individuals to live with more dignity and quality of life, with the necessary support for managing their chronic conditions and maintaining their autonomy.
References
Fernandes, R., Silva, S., & Costa, T. (2022). The relationship between frailty and chronic diseases in the elderly: A review of patient-centered care models. Journal of Geriatric Medicine, 40(2), 123-134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgm.2022.01.015
Lima, G., & Costa, F. (2022). The impact of chronic multimorbidity on geriatric care: Challenges and solutions. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 37(3), 299-308. https://doi.org/10.1002/gps.5782
Oliveira, L., Martins, J., & Pereira, R. (2021). Managing multimorbidity in older adults: A comprehensive approach to chronic diseases. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 34(5), 611-621. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocn.15673
Pereira, P., & Almeida, M. (2020). Family caregivers and the management of chronic diseases in the elderly: A training program proposal. Nursing and Care Research, 16(1), 44-52. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963731420926938
Rodrigues, A., Martins, M., & Silva, L. (2023). Public policies and long-term care for elderly patients with chronic conditions: Integrating care systems. Health Policy and Systems Review, 45(2), 210-220. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13603-023-00899-3
Sousa, M., Lima, R., & Santos, J. (2021). Telemedicine as a tool for chronic disease management in older adults: Benefits and limitations. Telemedicine and e-Health, 27(6), 652-658. https://doi.org/10.1089/tmj.2020.0546
Santos, F., & Ferreira, C. (2020). Multimorbidity in elderly patients: The need for a personalized care approach. Journal of Geriatric Care, 22(4), 334-342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgc.2020.03.005
Xu, X., Yang, H. (2022). Elderly chronic diseases and catastrophic health expenditure: an important cause of Borderline Poor Families’ return to poverty in rural China. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 9, 291. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-022-01310-5
Nursing Management, 27(6), 698–710.
Venturini, R. E. (2025). Technological innovations in agriculture: the application of Blockchain and Artificial Intelligence for grain traceability and protection. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(3), e78100. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n3-007
Turatti, R. C. (2025). Application of artificial intelligence in forecasting consumer behavior and trends in E-commerce. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(3), e78442. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n3-039
Garcia, A. G. (2025). The impact of sustainable practices on employee well-being and organizational success. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(3), e78599. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n3-054
Filho, W. L. R. (2025). The Role of Zero Trust Architecture in Modern Cybersecurity: Integration with IAM and Emerging Technologies. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(1), e76836. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n1-060
Antonio, S. L. (2025). Technological innovations and geomechanical challenges in Midland Basin Drilling. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(3), e78097. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n3-005
Moreira, C. A. (2025). Digital monitoring of heavy equipment: advancing cost optimization and operational efficiency. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(2), e77294. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n2-011
Delci, C. A. M. (2025). THE EFFECTIVENESS OF LAST PLANNER SYSTEM (LPS) IN INFRASTRUCTURE PROJECT MANAGEMENT. Revista Sistemática, 15(2), 133–139. https://doi.org/10.56238/rcsv15n2-009
SANTOS,Hugo;PESSOA,EliomarGotardi.Impactsofdigitalizationontheefficiencyandqualityofpublicservices:Acomprehensiveanalysis.LUMENETVIRTUS,[S.l.],v.15,n.40,p.44094414,2024.DOI:10.56238/levv15n40024.Disponívelem:https://periodicos.newsciencepubl.com/LEV/article/view/452.Acessoem:25jan.2025.
Freitas,G.B.,Rabelo,E.M.,&Pessoa,E.G.(2023).Projetomodularcomreaproveitamentodecontainermaritimo.BrazilianJournalofDevelopment,9(10),28303–28339.https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv9n10057
Freitas,G.B.,Rabelo,E.M.,&Pessoa,E.G.(2023).Projetomodularcomreaproveitamentodecontainermaritimo.BrazilianJournalofDevelopment,9(10),28303–28339.https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv9n10057
Pessoa,E.G.,Feitosa,L.M.,ePadua,V.P.,&Pereira,A.G.(2023).EstudodosrecalquesprimáriosemumaterroexecutadosobreaargilamoledoSarapuí.BrazilianJournalofDevelopment,9(10),28352–28375.https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv9n10059
PESSOA,E.G.;FEITOSA,L.M.;PEREIRA,A.G.;EPADUA,V.P.Efeitosdeespéciesdealnaeficiênciadecoagulação,Alresidualepropriedadedosflocosnotratamentodeáguassuperficiais.BrazilianJournalofHealthReview,[S.l.],v.6,n.5,p.2481424826,2023.DOI:10.34119/bjhrv6n5523.Disponívelem:https://ojs.brazilianjournals.com.br/ojs/index.php/BJHR/article/view/63890.Acessoem:25jan.2025.
SANTOS,Hugo;PESSOA,EliomarGotardi.Impactsofdigitalizationontheefficiencyandqualityofpublicservices:Acomprehensiveanalysis.LUMENETVIRTUS,[S.l.],v.15,n.40,p.44094414,2024.DOI:10.56238/levv15n40024.Disponívelem:https://periodicos.newsciencepubl.com/LEV/article/view/452.Acessoem:25jan.2025.
Filho, W. L. R. (2025). The Role of Zero Trust Architecture in Modern Cybersecurity: Integration with IAM and Emerging Technologies. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(1), e76836. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n1-060
Oliveira, C. E. C. de. (2025). Gentrification, urban revitalization, and social equity: challenges and solutions. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(2), e77293. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n2-010
Filho, W. L. R. (2025). THE ROLE OF AI IN ENHANCING IDENTITY AND ACCESS MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS. International Seven Journal of Multidisciplinary, 1(2). https://doi.org/10.56238/isevmjv1n2-011
Antonio, S. L. (2025). Technological innovations and geomechanical challenges in Midland Basin Drilling. Brazilian Journal of Development, 11(3), e78097. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv11n3-005.
